Microsoft PowerPoint - ch08_큐 [호환 모드]
|
|
|
- 창숙 조
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 큐 (Queue) 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조
2 이장에서다룰내용 1 큐 2 큐의구현 3 큐의응용 2
3 큐 (1) 큐 (Queue) 스택과마찬가지로삽입과삭제의위치가제한된유한순서리스트 큐의뒤에서는삽입만하고, 앞에서는삭제만할수있는구조 삽입한순서대로원소가나열되어가장먼저삽입 (First-In) 한원소는맨앞에있다가가장먼저삭제 (First-Out) 된다. 선입선출구조 (FIFO, First-In-First-Out) 스택과큐의구조비교 3
4 큐 (2) 큐의구조 4
5 큐 (3) 큐의연산 삽입 : enqueue 삭제 : dequeue 스택과큐의연산비교 5
6 큐 (4) 추상자료형큐 ADT Queue 데이터 : 0 개이상의원소를가진유한순서리스트연산 : Q Queue; item Element; createqueue() = create an empty Q; // 공백큐를생성하는연산 isempty(q) = if (Q is empty) then return true else return false; // 큐가공백인지아닌지를확인하는연산 enqueue(q, item) = insert item at the rear of Q; // 큐의 rear 에 item( 원소 ) 을삽입하는연산 dequeue(q) = if (isempty(q)) then return error else { delete and return the front itemof Q }; // 큐의 front 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을큐에서삭제하고반환하는연산 delete(q) = if (isempty(q)) then return error else { delete the front item of Q }; // 큐의 front 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을삭제하는연산 peek(q) = if (isempty(q)) then return error else { return the front item of the Q }; // 큐의 front 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을반환하는연산 End Queue [ADT 8-1] 6
7 큐 (5) 큐의연산과정 1 공백큐생성 : createqueue(); Q [0] [1] [2] front = rear = -1 2 원소 A 삽입 : enqueue(q, A); Q [0] [1] [2] A front = -1 rear 3 원소 B 삽입 : enqueue(q, B); Q [0] [1] [2] A B front = -1 rear 7
8 큐 (6) 4 원소삭제 : dequeue(q); Q A 5 원소 C 삽입 : enqueue(q, C); 6 원소삭제 : dequeue(q); 7 원소삭제 : dequeue(q); Q Q B Q C [0] [1] [2] A front B rear [0] [1] [2] B front [0] [1] [2] B front C rear C rear [0] [1] [2] C front rear 8
9 큐의구현 큐의구현 선형큐 (Linear Queue) 1차원배열을이용하여구현 원형큐 (Circular Queue) 선형큐의저장공간제한문제를해결 연결큐 (Linked-list Queue) 연결리스트를이용하여구현 9
10 선형큐의구현 (1) 선형큐 1 차원배열을이용한큐 큐의크기 = 배열의크기 변수 front : 저장된첫번째원소의인덱스저장 변수 rear : 저장된마지막원소의인덱스저장 상태표현 초기상태 : front = rear = -1 공백상태 : front = rear 포화상태 : rear = n-1 (n : 배열의크기, n-1 : 배열의마지막인덱스 ) 10
11 선형큐의구현 (2) 초기공백큐생성알고리즘 크기가 n인 1차원배열생성 front와 rear를 -1로초기화 createqueue() Q[n]; front -1; rear -1; end createqueue() [ 알고리즘 8-1] 11
12 선형큐의구현 (3) 공백큐검사알고리즘과포화상태검사알고리즘 공백상태 : front = rear 포화상태 : rear = n-1 (n : 배열의크기, n-1 : 배열의마지막인덱스 ) isempty(q) if(front=rear) then return true; else return false; end isempty() [ 알고리즘 8-2] isfull(q) if(rear=n-1) then return true; else return false; end isfull() 12
13 선형큐의구현 (4) 큐의삽입알고리즘 enqueue(q, item) if(isfull(q)) then Queue_Full(); else { rear rear+1; // ❶ Q[rear] item; // ❷ } end enqueue() [ 알고리즘 8-3] 마지막원소의뒤에삽입해야하므로 1 마지막원소의인덱스를저장한 rear 의값을하나증가시켜삽입할자리준비 2 그인덱스에해당하는배열원소 Q[rear] 에 item 을저장 13
14 선형큐의구현 (5) 큐의삭제알고리즘 dequeue(q) if(isempty(q)) then Queue_Empty(); else { front front+1; // ❶ return Q[front]; // ❷ } end dequeue() [ 알고리즘 8-4] delete(q) if(isempty(q)) then Queue_Empty(); else front front+1; end delete() 가장앞에있는원소를삭제해야하므로 1 front 의위치를한자리뒤로이동하여큐에남아있는첫번째원소의위치로이동하여삭제할자리준비 2 그자리의원소를삭제하여반환 14
15 선형큐의구현 (6) 큐의검색알고리즘 peek(q) if(isempty(q)) then Queue_Empty(); else return Q[front+1]; end peek() [ 알고리즘 8-5] 가장앞에있는원소를검색하여반환하는연산 1 현재 front 의한자리뒤 (front+1) 에있는원소, 즉큐에있는첫번째원소를반환 15
16 선형큐의구현 (7) 순차자료구조방식으로구현한큐프로그램 001 interface Queue{ 002 boolean isempty(); 003 void enqueue(char item); 004 char dequeue(); 005 void delete(); 006 char peek(); 007 } class ArrayQueue implements Queue{ 010 private int front; 011 private int rear; 012 private int queuesize; 013 private char itemarray[]; public ArrayQueue(int queuesize){ 016 front = -1; 017 rear = -1; [ 예제 5-4] >> 계속 16
17 선형큐의구현 (8) 018 this.queuesize = queuesize; [ 예제 5-4] 019 itemarray = new char[this.queuesize]; 020 } public boolean isempty(){ 023 return (front == rear); 024 } public boolean isfull(){ 027 return (rear == this.queuesize-1); 028 } public void enqueue(char item){ 031 if(isfull()){ 032 System.out.println("Inserting fail! Array Queue is full!!"); 033 } 034 else{ 035 itemarray[++rear] = item; >> 계속 17
18 선형큐의구현 (9) 036 System.out.println("Inserted Item : " + item); [ 예제 5-4] 037 } 038 } public char dequeue(){ 041 if(isempty()) { 042 System.out.println("Deleting fail! Array Queue is empty!!"); 043 return 0; 044 } 045 else{ 046 return itemarray[++front]; 047 } } public void delete(){ 052 if(isempty()){ 053 System.out.println("Deleting fail! Array Queue is empty!!"); >> 계속 18
19 선형큐의구현 (10) 054 [ 예제 5-4] 055 } 056 else { front; 058 } 059 } public char peek(){ 062 if(isempty()){ 063 System.out.println("Peeking fail! Array Queue is empty!!"); 064 return 0; 065 } 066 else 067 return itemarray[front+1]; 068 } public void printqueue(){ 071 if(isempty()) >> 계속 19
20 선형큐의구현 (11) 072 System.out.printf("Array Queue is empty!! %n %n"); 073 else{ 074 System.out.printf("Array Queue>> "); 075 for(int i=front+1; i<=rear; i++) 076 System.out.printf("%c ", itemarray[i]); 077 System.out.println();System.out.println(); 078 } 079 } } class Ex8_1{ 084 public static void main(string args[]){ 085 int queuesize = 3; 086 char deleteditem; 087 ArrayQueue Q = new ArrayQueue(queueSize); Q.enQueue('A'); [ 예제 5-4] >> 계속 20
21 선형큐의구현 (12) 090 Q.printQueue(); Q.enQueue('B'); 093 Q.printQueue(); deleteditem = Q.deQueue(); 096 if(deleteditem!= 0) 097 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 098 Q.printQueue(); Q.enQueue('C'); 101 Q.printQueue(); deleteditem = Q.deQueue(); 104 if(deleteditem!= 0) 105 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 106 Q.printQueue(); 107 [ 예제 5-4] >> 계속 21
22 선형큐의구현 (13) 108 deleteditem = Q.deQueue(); 109 if(deleteditem!= 0) 110 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 111 Q.printQueue(); deleteditem = Q.deQueue(); 114 if(deleteditem!= 0) 115 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 116 Q.printQueue(); 117 } 118 } [ 예제 5-4] >> 계속 22
23 선형큐의구현 (14) 실행결과 23
24 원형큐의구현 (1) 원형큐 선형큐의잘못된포화상태인식 큐에서삽입과삭제를반복하면서아래와같은상태일경우, 앞부분에빈자리가있지만 rear=n-1 상태이므로포화상태로인식하고더이상의삽입을수행하지않는다. 선형큐의잘못된포화상태인식의해결방법 -1 저장된원소들을배열의앞부분으로이동시키기 순차자료에서의이동작업은연산이복잡하여효율성이떨어짐 24
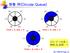
25 원형큐의구현 (2) 선형큐의잘못된포화상태인식의해결방법-2 1차원배열을사용하면서논리적으로배열의처음과끝이연결되어있다고가정하고사용 원형큐의논리적구조 25
26 원형큐의구현 [3) 원형큐의구조 초기공백상태 : front = rear = 0 front와 rear의위치가배열의마지막인덱스 n-1에서논리적인다음자리인인덱스 0번으로이동하기위해서나머지연산자 mod를사용 3 4 = 0 3 ( 몫 =0, 나머지 =3) 3 mod 4 = 3 공백상태와포화상태구분을쉽게하기위해서 front 가있는자리는사용하지않고항상빈자리로둔다. 26
27 원형큐의구현 (4) 초기공백원형큐생성알고리즘 크기가 n인 1차원배열생성 front와 rear를 0 으로초기화 createqueue() cq[n]; front 0; rear 0; end createqueue() [ 알고리즘 8-6] 27
28 원형큐의구현 (5) 원형큐의공백상태검사알고리즘과포화상태검사알고리즘 공백상태 : front = rear 포화상태 : 삽입할 rear 의다음위치 = front 의현재위치 (rear+1) mod n = front isempty(cq) if(front=rear) then return true; else return false; end isempty() [ 알고리즘 8-7] isfull(cq) if(((rear+1) mod n)=front) then return true; else return false; end isfull() 28
29 원형큐의구현 (6) 원형큐의삽입알고리즘 1 rear의값을조정하여삽입할자리를준비 : rear (rear+1) mod n; 2 준비한자리 cq[rear] 에원소 item을삽입 enqueue(cq, item) if(isfull(cq)) then Queue_Full(); else { rear (rear+1) mod n; // ❶ cq[rear] item; // ❷ } end enqueue() [ 알고리즘 8-8] 29
30 원형큐의구현 (7) 원형큐의삭제알고리즘 1front의값을조정하여삭제할자리를준비 2 준비한자리에있는원소 cq[front] 를삭제하여반환 dequeue(cq) if(isempty(cq)) then Queue_Empty(); else { front (front+1) mod n; // ❶ return cq[front]; // ❷ } end dequeue() [ 알고리즘 8-9] delete(cq) if(isempty(q)) then Queue_Empty(); else front (front+1) mod n; end delete() 30
31 원형큐의구현 (8) 원형큐에서의연산과정 1 createqueue(); 2 enqueue(cq, A); [1] [2] rear [1] [2] A [0] [3] front rear [0] front [3] 31
32 원형큐의구현 (9) 3 enqueue(cq, B); rear 4 dequeue(cq); front rear [1] [2] A B [1] [2] A B [0] [3] [0] [3] front 5 enqueue(cq, C); front 6 enqueue(cq, D); front [1] [2] B [1] [2] B [0] C [3] [0] D C [3] rear rear 32
33 원형큐의구현 (10) 순차자료구조방식으로구현한원형큐프로그램 001 interface Queue{ 002 boolean isempty(); 003 void enqueue(char item); 004 char dequeue(); 005 void delete(); 006 char peek(); 007 } class ArrayCQueue implements Queue{ 010 private int front; 011 private int rear; 012 private int queuesize; 013 private char itemarray[]; public ArrayCQueue(int queuesize){ 016 front = 0; 017 rear = 0; [ 예제 5-4] >> 계속 33
34 원형큐의구현 (11) 018 this.queuesize = queuesize; [ 예제 5-4] 019 itemarray = new char[this.queuesize]; 020 } public boolean isempty(){ 023 return (front == rear); 024 } public boolean isfull(){ 027 return (((rear+1) % this.queuesize) == front); 028 } public void enqueue(char item){ 031 if(isfull()){ 032 System.out.println("Inserting fail! Array Circular Queue is full!!"); 033 } 034 else{ 035 rear = (rear+1) % this.queuesize; >> 계속 34
35 원형큐의구현 (12) 036 itemarray[rear] = item; [ 예제 5-4] 037 System.out.println("Inserted Item : " + item); 038 } 039 } public char dequeue(){ 042 if(isempty()) { 043 System.out.println("Deleting fail! Array Circular Queue is empty!!"); 044 return 0; 045 } 046 else{ 047 front = (front+1) % this.queuesize; 048 return itemarray[front]; 049 } } public void delete(){ >> 계속 35
36 원형큐의구현 (13] 054 if(isempty()){ [ 예제 5-4] 055 System.out.println("Deleting fail! Array Circular Queue is empty!!"); } 058 else { 059 front = (front+1) % this.queuesize; 060 } 061 } public char peek(){ 064 if(isempty()){ 065 System.out.println("Peeking fail! Array Circular Queue is empty!!"); 066 return 0; 067 } 068 else 069 return itemarray[(front+1) % this.queuesize]; 070 } 071 >> 계속 36
37 원형큐의구현 (14] 072 public void printqueue(){ [ 예제 5-4] 073 if(isempty()) 074 System.out.println("Array Circular Queue is empty!!"); 075 else{ 076 System.out.printf("Array Circular Queue>> "); 077 for(int i=(front+1) % this.queuesize; i!=(rear+1)% this.queuesize; i=++i % this.queuesize) 078 System.out.printf("%c ", itemarray[i]); 079 System.out.println(); System.out.println(); 080 } 081 } } class Ex8_2{ 087 public static void main(string args[]){ 088 int queuesize = 4; >> 계속 37
38 원형큐의구현 (15) 089 char deleteditem; 090 ArrayCQueue cq = new ArrayCQueue(queueSize); cq.enqueue('a'); 093 cq.printqueue(); cq.enqueue('b'); 096 cq.printqueue(); deleteditem = cq.dequeue(); 099 if(deleteditem!= 0) 100 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 101 cq.printqueue(); cq.enqueue('c'); 104 cq.printqueue(); cq.enqueue('d'); [ 예제 5-4] >> 계속 38
39 원형큐의구현 (16) 107 cq.printqueue(); cq.enqueue('e'); 110 cq.printqueue(); 111 } 112 } [ 예제 5-4] 실행결과 39
40 연결큐의구현 (1) 연결큐 단순연결리스트를이용한큐 큐의원소 : 단순연결리스트의노드 큐의원소의순서 : 노드의링크포인터로연결 변수 front : 첫번째노드를가리키는포인터변수 변수 rear : 마지막노드를가리키는포인터변수 상태표현 초기상태와공백상태 : front = rear = null 연결큐의구조 40
41 연결큐의구현 (2) 초기공백연결큐생성알고리즘 초기화 : front = rear = null createlinkedqueue() front null; rear null; end createlinkedqueue() [ 알고리즘 8-10] 41
42 연결큐의구현 (3) 공백연결큐검사알고리즘 공백상태 : front = rear = null isempty(lq) if(front=null) then return true; else return false; end isempty() [ 알고리즘 8-11] 42
43 연결큐의구현 (4) 연결큐의삽입알고리즘 enqueue(lq, item) new getnode(); new.data item; // ❶ new.link null; if (isempty(lq)) then { // ❷ 연결큐가공백인경우 rear new; front new; } else { // ❸ 연결큐에노드가있는경우 rear.link new; rear new; } end enqueue() [ 알고리즘 8-12] 43
44 연결큐의구현 (5) 1 삽입할새노드를생성하여데이터필드에 item 을저장한다. 삽입할새노드는연결큐의마지막노드가되어야하므로링크필드에 null 을저장한다. 2 새노드를삽입하기전에연결큐가공백인지아닌지를검사한다. 연결큐가공백인경우에는삽입할새노드가큐의첫번째노드이자마지막노드이므로포인터 front와 rear가모두새노드를가리키도록설정한다. 44
45 연결큐의구현 (6) 3 큐가공백이아닌경우, 즉노드가있는경우에는현재큐의마지막노드의뒤에새노드를삽입하고마지막노드를가리키는 rear가삽입한새노드를가리키도록설정한다. 45
46 연결큐의구현 (7) 연결큐의삭제알고리즘 dequeue(lq) if(isempty(lq)) then Queue_Empty(); else { old front; // ❶ item front.data; front front.link; // ❷ if (isempty(lq)) then rear null; // ❸ returnnode(old); // ❹ return item; } end dequeue() [ 알고리즘 8-13] delete(lq) if(isempty(lq)) then Queue_Empty(); else { old front; front front.link; if(isempty(lq)) then rear null; returnnode(old); } end delete() 46
47 연결큐의구현 (8) 1 삭제연산에서삭제할노드는큐의첫번째노드로서포인터 front가가리키고있는노드이다. front가가리키는노드를포인터 old가가리키게하여삭제할노드를지정한다. 2 삭제연산후에는현재 front 노드의다음노드가 front 노드 ( 첫번째노드 ) 가되어야하므로, 포인터 front를재설정한다. 47
48 연결큐의구현 (9) 3 현재큐에노드가하나뿐이어서삭제연산후에공백큐가되는경우 : 큐의마지막노드가없어지므로포인터 rear 를 null 로설정한다. 4 포인터 old가가리키고있는노드를삭제하고, 메모리공간을시스템에반환 (returnnode()) 한다 48
49 연결큐의구현 (10) 연결큐의검색알고리즘 연결큐의첫번째노드, 즉 front 노드의데이터필드값을반환 peek(lq) if(isempty(lq)) then Queue_Empty() else return (front.data); end peek() [ 알고리즘 8-14] 49
50 연결큐의구현 (11) 연결큐에서의연산과정 1 공백큐생성 : createlinkedqueue(); 2 원소 A 삽입 : enqueue(lq, A); 3 원소 B 삽입 : enqueue(lq, B); 50
51 연결큐의구현 (12) 4 원소삭제 : dequeue(lq); 5 원소 C 삽입 : enqueue(lq, C); 51
52 연결큐의구현 (13) 6 원소삭제 : dequeue(lq); 7 원소삭제 : dequeue(lq); 52
53 연결큐의구현 (14) 연결자료구조방식을이용하여구현한연결큐프로그램 001 interface Queue{ 002 boolean isempty(); 003 void enqueue(char item); 004 char dequeue(); 005 void delete(); 006 char peek(); 007 } class QNode{ 010 char data; 011 QNode link; 012 } class LinkedQueue implements Queue{ 015 QNode front; 016 QNode rear; 017 [ 예제 8-3] >> 계속 53
54 연결큐의구현 (15) 018 public LinkedQueue(){ 019 front = null; 020 rear = null; 021 } public boolean isempty(){ 024 return (front == null); 025 } public void enqueue(char item){ 028 QNode newnode = new QNode(); 029 newnode.data = item; 030 newnode.link = null; 031 if(isempty()){ 032 front = newnode; 033 rear = newnode; 034 } 035 else { [ 예제 8-3] >> 계속 54
55 연결큐의구현 (16) 036 rear.link = newnode; [ 예제 8-3] 037 rear = newnode; 038 } 039 System.out.println("Inserted Item : " + item); 040 } public char dequeue(){ 043 if(isempty()) { 044 System.out.println("Deleting fail! Linked Queue is empty!!"); 045 return 0; 046 } 047 else{ 048 char item = front.data; 049 front = front.link; 050 if(front == null) 051 rear = null; 052 return item; 053 } >> 계속 55
56 연결큐의구현 (17) 054 } [ 예제 8-3] public void delete(){ 057 if(isempty()){ 058 System.out.println("Deleting fail! Linked Queue is empty!!"); 059 } else { 062 front = front.link; 063 if(front == null) 064 rear = null; 065 } 066 } public char peek(){ 069 if(isempty()){ 070 System.out.println("Peeking fail! Linked Queue is empty!!"); 071 return 0; >> 계속 56
57 연결큐의구현 (18) 072 } 073 else 074 return front.data; 075 } public void printqueue(){ 078 if(isempty()) 079 System.out.printf("Linked Queue is empty!! %n %n"); 080 else{ 081 QNode temp = front; 082 System.out.printf("Linked Queue>> "); 083 while(temp!= null){ 084 System.out.printf("%c ", temp.data); 085 temp = temp.link; 086 } 087 System.out.println();System.out.println(); 088 } 089 } [ 예제 8-3] >> 계속 57
58 연결큐의구현 (19) 090 } class Ex8_3{ 093 public static void main(string args[]){ 094 char deleteditem; 095 LinkedQueue LQ = new LinkedQueue(); LQ.enQueue('A'); 098 LQ.printQueue(); LQ.enQueue('B'); 101 LQ.printQueue(); deleteditem = LQ.deQueue(); 104 if(deleteditem!= 0) 105 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 106 LQ.printQueue(); 107 [ 예제 8-3] >> 계속 58
59 연결큐의구현 (20) 108 LQ.enQueue('C'); 109 LQ.printQueue(); deleteditem = LQ.deQueue(); 112 if(deleteditem!= 0) 113 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 114 LQ.printQueue(); deleteditem = LQ.deQueue(); 117 if(deleteditem!= 0) 118 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 119 LQ.printQueue(); deleteditem = LQ.deQueue(); 122 if(deleteditem!= 0) 123 System.out.println("deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 124 LQ.printQueue(); 125 } 126 } [ 예제 8-3] 59
60 연결큐의구현 (21) 실행결과 60
61 덱 (Deque) (1) 덱 (Deque, double-ended queue) 큐 2 개를반대로붙여서만든자료구조 Queue-1 삭제 삽입 삽입 삭제 Queue-2 삽입 삭제 Deque 삽입 삭제 front 저장된원소중에서가장앞부분원소 rear 저장된원소중에서가장뒷부분원소 61
62 덱 (Deque) (2) 덱에대한추상자료형 ADT deque 데이터 : 0 개이상의원소를가진유한순서리스트연산 : DQ deque; item Element; createdeque() = create an empty DQ; // 공백덱을생성하는연산 isempty(dq) = if (DQ is empty) then return true else return false; // 덱이공백인지아닌지를확인하는연산 insertfront(dq, item) = insert item at the front of DQ; // 덱의 front 앞에 item( 원소 ) 을삽입하는연산 insertrear(dq, item) = insert item at the rear of DQ; // 덱의 rear 뒤에 item( 원소 ) 을삽입하는연산 deletefront(dq) = if (isempty(dq)) then return null else { delete and return the front item of DQ }; // 덱의 front 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을덱에서삭제하고반환하는연산 deleterear(dq) = if (isempty(dq)) then return null else { delete and return the rear item of DQ }; [ADT 8-2] 62
63 덱 (Deque) (3) // 덱의 rear 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을덱에서삭제하고반환하는연산 removefront(dq) = if (isempty(dq)) then return null else { remove the front item of DQ }; // 덱의 front 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을삭제하는연산 removerear(dq) = if (isempty(dq)) then return null else { remove the rear item of DQ }; // 덱의 rear 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을삭제하는연산 peekfront(dq) = if (isempty(dq)) then return null else { return the front item of the DQ }; // 덱의 front 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을반환하는연산 peekrear(dq) = if (isempty(dq)) then return null else { return the rear item of the DQ }; // 덱의 rear 에있는 item( 원소 ) 을반환하는연산 End deque [ADT 8-2] 63
64 덱 (Deque) (4) 덱에서의연산과정 1 createdeque(); DQ front rear 2 insertfront(dq, 'A'); DQ A front rear 3 insertfront(dq, 'B'); DQ B A front rear 4 insertrear(dq, 'C'); DQ B A C front rear 64
65 덱 (Deque) (5) 5 deletefront(dq); B front DQ A C rear 6 deleterear(dq); DQ A C front rear 7 insertrear(dq, 'D'); DQ A D front rear 8 insertfront(dq, 'E'); DQ E A D front rear 65
66 덱 (Deque) (6) 9 insertfront(dq, 'F'); DQ F E A D front rear 덱의구현 양쪽끝에서삽입 / 삭제연산을수행하면서크기변화와저장된원소의순서변화가많으므로순차자료구조는비효율적 양방향으로연산이가능한이중연결리스트를사용한다. 66
67 덱의구현 (1) 이중연결리스트를이용한덱프로그램 001 class DQNode{ 002 char data; 003 DQNode rlink; 004 DQNode llink; 005 } class DQueue{ 008 DQNode front; 009 DQNode rear; public DQueue(){ 012 front = null; 013 rear = null; 014 } public boolean isempty(){ 017 return (front == null); [ 예제 8-4] >> 계속 67
68 덱의구현 (2) 018 } public void insertfront(char item){ 021 DQNode newnode = new DQNode(); 022 newnode.data = item; 023 if(isempty()){ 024 front = newnode; 025 rear = newnode; 026 newnode.rlink = null; 027 newnode.llink = null; 028 } 029 else { 030 front.llink = newnode; 031 newnode.rlink = front; 032 newnode.llink = null; 033 front = newnode; 034 } 035 System.out.println("Front Inserted Item : " + item); [ 예제 8-4] >> 계속 68
69 덱의구현 (3) 036 } public void insertrear(char item){ 039 DQNode newnode = new DQNode(); 040 newnode.data = item; 041 if(isempty()){ 042 front = newnode; 043 rear = newnode; 044 newnode.rlink = null; 045 newnode.llink = null; 046 } 047 else { 048 rear.rlink = newnode; 049 newnode.rlink = null; 050 newnode.llink = rear; 051 rear = newnode; 052 } 053 System.out.println("Rear Inserted Item : " + item); [ 예제 8-4] >> 계속 69
70 덱의구현 (4) 054 } [ 예제 8-4] public char deletefront(){ 057 if(isempty()) { 058 System.out.println("Front Deleting fail! Dqueue is empty!!"); 059 return 0; 060 } 061 else{ 062 char item = front.data; 063 if(front.rlink == null){ 064 front = null; 065 rear = null; 066 } 067 else { 068 front = front.rlink; 069 front.llink = null; 070 } 071 return item; >> 계속 70
71 덱의구현 (5) 072 } [ 예제 8-4] 073 } public char deleterear(){ 076 if(isempty()) { 077 System.out.println("Rear Deleting fail! Dqueue is empty!!"); 078 return 0; 079 } 080 else{ 081 char item = rear.data; 082 if(rear.llink == null){ 083 rear = null; 084 front = null; 085 } 086 else { 087 rear = rear.llink; 088 rear.rlink = null; 089 } >> 계속 71
72 덱의구현 (6) 090 return item; [ 예제 8-4] 091 } 092 } public void removefront(){ 095 if(isempty()) { 096 System.out.println("Front Removing fail! Dqueue is empty!!"); 097 } 098 else{ 099 if(front.rlink == null){ 100 front = null; 101 rear = null; 102 } 103 else { 104 front = front.rlink; 105 front.llink = null; 106 } 107 } >> 계속 72
73 덱의구현 (7) 108 } [ 예제 8-4] public void removerear(){ 111 if(isempty()) { 112 System.out.println("Rear Removing fail! Dqueue is empty!!"); 113 } 114 else{ 115 if(rear.llink == null){ 116 rear = null; 117 front = null; 118 } 119 else { 120 rear = rear.llink; 121 rear.rlink = null; 122 } 123 } 124 } 125 >> 계속 73
74 덱의구현 (8) 126 public char peekfront(){ [ 예제 8-4] 127 if(isempty()){ 128 System.out.println("Front Peeking fail! DQueue is empty!!"); 129 return 0; 130 } 131 else 132 return front.data; 133 } public char peekrear(){ 136 if(isempty()){ 137 System.out.println("Rear Peeking fail! DQueue is empty!!"); 138 return 0; 139 } 140 else 141 return rear.data; 142 } 143 >> 계속 74
75 덱의구현 (9) 144 public void printdqueue(){ 145 if(isempty()) 146 System.out.printf("DQueue is empty!! %n %n"); 147 else{ 148 DQNode temp = front; 149 System.out.printf("DQueue>> "); 150 while(temp!= null){ 151 System.out.printf("%c ", temp.data); 152 temp = temp.rlink; 153 } 154 System.out.println(); System.out.println(); 155 } 156 } 157 } class Ex8_4{ 160 public static void main(string args[]){ 161 char deleteditem; [ 예제 8-4] >> 계속 75
76 덱의구현 (10) 162 DQueue DQ = new DQueue(); [ 예제 8-4] DQ.insertFront('A'); 165 DQ.printDQueue(); DQ.insertFront('B'); 168 DQ.printDQueue(); DQ.insertRear('C'); 171 DQ.printDQueue(); deleteditem = DQ.deleteFront(); 174 if(deleteditem!= 0) 175 System.out.println("Front deleted Item : " + deleteditem); 176 DQ.printDQueue(); deleteditem = DQ.deleteRear(); 179 if(deleteditem!= 0) >> 계속 76
77 덱의구현 (11) 180 System.out.println("Rear deleted Item : " + deleteditem); [ 예제 8-4] 181 DQ.printDQueue(); DQ.insertRear('D'); 184 DQ.printDQueue(); DQ.insertFront('E'); 187 DQ.printDQueue(); DQ.insertFront('F'); 190 DQ.printDQueue(); 191 } 192 } >> 계속 77
78 덱의구현 (12) 실행결과 78
79 큐의응용 운영체제의작업큐 프린터버퍼큐 CPU에서프린터로보낸데이터순서대로 ( 선입선출 ) 프린터에서출력하기위해서선입선출구조의큐사용 스케줄링큐 CPU 사용을요청한프로세서들의순서를스케줄링하기위해큐를사용 79
80 큐의응용 시뮬레이션큐잉시스템 시뮬레이션을위한수학적모델링에서대기행렬과대기시간등을모델링하기위해서큐잉이론 (Queue theory) 사용 80
81 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조
Contents v 학습목표 자료구조큐에대한개념을스택과비교하여이해한다. 큐의특징과연산방법에대해알아본다. 순차표현방법을이용한큐와연결표현방법을이용한큐를구현해본다. 큐의응용방법을알아본다. v 내용 큐 큐의구현 큐의응용 2/74
 큐 IT CookBook, C 로배우는쉬운자료구조 ( 개정판 ) Contents v 학습목표 자료구조큐에대한개념을스택과비교하여이해한다. 큐의특징과연산방법에대해알아본다. 순차표현방법을이용한큐와연결표현방법을이용한큐를구현해본다. 큐의응용방법을알아본다. v 내용 큐 큐의구현 큐의응용 2/74 1. 큐 v 큐 (Queue) 데이터의삽입과삭제가양쪽끝에서일어나는자료구조
큐 IT CookBook, C 로배우는쉬운자료구조 ( 개정판 ) Contents v 학습목표 자료구조큐에대한개념을스택과비교하여이해한다. 큐의특징과연산방법에대해알아본다. 순차표현방법을이용한큐와연결표현방법을이용한큐를구현해본다. 큐의응용방법을알아본다. v 내용 큐 큐의구현 큐의응용 2/74 1. 큐 v 큐 (Queue) 데이터의삽입과삭제가양쪽끝에서일어나는자료구조
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 6: 큐 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 Ticket Box 전단 () 후단 () 2 큐 ADT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO 순서를따른다. 삽입은큐의후단에서, 삭제는전단에서이루어진다. 객체 : n 개의 element
CHAP 6: 큐 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 Ticket Box 전단 () 후단 () 2 큐 ADT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO 순서를따른다. 삽입은큐의후단에서, 삭제는전단에서이루어진다. 객체 : n 개의 element
2. QUEUE OPERATIONS Initialize the queue Insert to the rear of the queue (also called as Enqueue) Remove (Delete) from the front of the queue (also ca
 Queues The name "queue" likely comes from the everyday use of the term. Consider: queue of people waiting at a bus stop, as pictured in fig. below. Each new person who comes and takes his or her place
Queues The name "queue" likely comes from the everyday use of the term. Consider: queue of people waiting at a bus stop, as pictured in fig. below. Each new person who comes and takes his or her place
슬라이드 1
 CHP 6: 큐 C 로쉽게풀어쓴자료구조 생능출판사 2005 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 Ticket Box 전단 () 후단 () 큐 DT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO 순서를따른다. 삽입은큐의후단에서, 삭제는전단에서이루어진다. 객체 : n 개의 element
CHP 6: 큐 C 로쉽게풀어쓴자료구조 생능출판사 2005 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 Ticket Box 전단 () 후단 () 큐 DT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO 순서를따른다. 삽입은큐의후단에서, 삭제는전단에서이루어진다. 객체 : n 개의 element
Microsoft PowerPoint - 08-chap06-Queue.ppt
 / 큐 (QUEUE) Chapter 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 큐 Ticket ox Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr Department of Kunsan National University 전단 () 후단 () 학습목표 큐 DT 큐의개념및추상데이터타입에대한이해
/ 큐 (QUEUE) Chapter 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 큐 Ticket ox Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr Department of Kunsan National University 전단 () 후단 () 학습목표 큐 DT 큐의개념및추상데이터타입에대한이해
Microsoft PowerPoint - 08-Queue.ppt
 Chapter Queue ( 큐 ) Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr Department of Informatics & Statistics 학습목표 큐의개념및추상데이터타입에대한이해 큐의구현방법 배열 링크드리스트 덱 / 데크의개념과구현방법 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In
Chapter Queue ( 큐 ) Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr Department of Informatics & Statistics 학습목표 큐의개념및추상데이터타입에대한이해 큐의구현방법 배열 링크드리스트 덱 / 데크의개념과구현방법 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 6: 큐 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 Ticket Box 전단 (front) 후단 (rear) 큐 ADT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO 순서를따른다. 삽입은큐의후단에서, 삭제는전단에서이루어진다. 객체 : n 개의 element 형으로구성된요소들의순서있는모임
CHAP 6: 큐 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 Ticket Box 전단 (front) 후단 (rear) 큐 ADT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO 순서를따른다. 삽입은큐의후단에서, 삭제는전단에서이루어진다. 객체 : n 개의 element 형으로구성된요소들의순서있는모임
Algorithms
 자료구조 & 알고리즘 스택과큐 (Stack and Queue) Seo, Doo-okok clickseo@gmail.com http://www.clickseo.com 목 차 스택의개념및구현 큐의개념및구현 2 스택 스택의개념및구현 스택의구현 스택의응용 큐의개념및구현 3 스택 (Stack) 스택의구조 후입선출 (LIFO, Last-In-First-Out) 삽입 PUSH
자료구조 & 알고리즘 스택과큐 (Stack and Queue) Seo, Doo-okok clickseo@gmail.com http://www.clickseo.com 목 차 스택의개념및구현 큐의개념및구현 2 스택 스택의개념및구현 스택의구현 스택의응용 큐의개념및구현 3 스택 (Stack) 스택의구조 후입선출 (LIFO, Last-In-First-Out) 삽입 PUSH
o 스택 (stack) ~ 쌓아놓은더미 1. 스택의개요 - 2 -
 스택 (stack) SANGJI University Kwangman Ko o 스택 (stack) ~ 쌓아놓은더미 1. 스택의개요 - 2 - o 스택의특징 ~ 모든원소의삽입과삭제가 top 이라는자료구조의한쪽끝에서만수행되는제한된리스트구조 ~ 후입선출 (Last-In-First-Out, LIFO) 방식 가장마지막에입력된자료가가장먼저출력 o 스택의동작 ~ top 에서만삽입
스택 (stack) SANGJI University Kwangman Ko o 스택 (stack) ~ 쌓아놓은더미 1. 스택의개요 - 2 - o 스택의특징 ~ 모든원소의삽입과삭제가 top 이라는자료구조의한쪽끝에서만수행되는제한된리스트구조 ~ 후입선출 (Last-In-First-Out, LIFO) 방식 가장마지막에입력된자료가가장먼저출력 o 스택의동작 ~ top 에서만삽입
04장.큐
 ---------------- DATA STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- CHAPTER 큐 1/33 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 A B C 전단 ( front) 후단 ( rea r) 2/33 큐 ADT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO
---------------- DATA STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- CHAPTER 큐 1/33 큐 (QUEUE) 큐 : 먼저들어온데이터가먼저나가는자료구조 선입선출 (FIFO: First-In First-Out) ( 예 ) 매표소의대기열 A B C 전단 ( front) 후단 ( rea r) 2/33 큐 ADT 삽입과삭제는 FIFO
03_queue
 Queue Data Structures and Algorithms 목차 큐의이해와 ADT 정의 큐의배열기반구현 큐의연결리스트기반구현 큐의활용 덱 (Deque) 의이해와구현 Data Structures and Algorithms 2 큐의이해와 ADT 정의 Data Structures and Algorithms 3 큐 (Stack) 의이해와 ADT 정의 큐는 LIFO(Last-in,
Queue Data Structures and Algorithms 목차 큐의이해와 ADT 정의 큐의배열기반구현 큐의연결리스트기반구현 큐의활용 덱 (Deque) 의이해와구현 Data Structures and Algorithms 2 큐의이해와 ADT 정의 Data Structures and Algorithms 3 큐 (Stack) 의이해와 ADT 정의 큐는 LIFO(Last-in,
Algorithms
 자료구조 & 알고리즘 리스트 (List) Seo, Doo-okok clickseo@gmail.com http://www.clickseo.com 목 차 선형리스트 연결리스트 2 선형리스트 선형리스트 선형리스트의개념 선형리스트의구현 연결리스트 3 선형리스트개념 리스트 (List) 목록, 대부분의목록은도표 (Table) 형태로표시 추상자료형리스트는이러한목록또는도표를추상화한것
자료구조 & 알고리즘 리스트 (List) Seo, Doo-okok clickseo@gmail.com http://www.clickseo.com 목 차 선형리스트 연결리스트 2 선형리스트 선형리스트 선형리스트의개념 선형리스트의구현 연결리스트 3 선형리스트개념 리스트 (List) 목록, 대부분의목록은도표 (Table) 형태로표시 추상자료형리스트는이러한목록또는도표를추상화한것
Microsoft PowerPoint - ch07_스택 [호환 모드]
![Microsoft PowerPoint - ch07_스택 [호환 모드] Microsoft PowerPoint - ch07_스택 [호환 모드]](/thumbs/82/85983214.jpg) 스택 (Stack) 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조 이장에서다룰내용 1 스택 2 스택의추상자료형 3 스택의구현 4 스택의응용 2 스택 (1) 스택 (stack) 접시를쌓듯이자료를차곡차곡쌓아올린형태의자료구조 스택에저장된원소는 top 으로정한곳에서만접근가능 top 의위치에서만원소를삽입하므로먼저삽입한원소는밑에쌓이고, 나중에삽입한원소는위에쌓인다. 마지막에삽입 (Last-In)
스택 (Stack) 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조 이장에서다룰내용 1 스택 2 스택의추상자료형 3 스택의구현 4 스택의응용 2 스택 (1) 스택 (stack) 접시를쌓듯이자료를차곡차곡쌓아올린형태의자료구조 스택에저장된원소는 top 으로정한곳에서만접근가능 top 의위치에서만원소를삽입하므로먼저삽입한원소는밑에쌓이고, 나중에삽입한원소는위에쌓인다. 마지막에삽입 (Last-In)
06장.리스트
 ---------------- DATA STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- CHAPTER 리스트 1/28 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list) 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 :
---------------- DATA STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- CHAPTER 리스트 1/28 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list) 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 :
untitled
 - -, (insert) (delete) - - (insert) (delete) (top ) - - (insert) (rear) (delete) (front) A A B top A B C top push(a) push(b) push(c) A B top pop() top A B D push(d) top #define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100 int
- -, (insert) (delete) - - (insert) (delete) (top ) - - (insert) (rear) (delete) (front) A A B top A B C top push(a) push(b) push(c) A B top pop() top A B D push(d) top #define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100 int
Chapter 4. LISTS
 C 언어에서리스트구현 리스트의생성 struct node { int data; struct node *link; ; struct node *ptr = NULL; ptr = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node)); Self-referential structure NULL: defined in stdio.h(k&r C) or
C 언어에서리스트구현 리스트의생성 struct node { int data; struct node *link; ; struct node *ptr = NULL; ptr = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node)); Self-referential structure NULL: defined in stdio.h(k&r C) or
Microsoft PowerPoint - 제4장-스택과큐.pptx
 제 4 강의. 스택과큐자료구조 1 제 4 강. 스택과큐자료구조 학습목차 1. 스택과큐자료구조 2. 스택자료구조 3. 큐자료구조 4. 원형큐의구현 2 1. 스택 (Stack) 과큐자료구조 리스트, 스택과큐 (Stack and Queue) 스택과큐는리스트자료구조의특별한경우이다. 리스트 - 순서가있다 - 읽기, 삽입 (insert) 과삭제 (delete) 를리스트의어느곳에서나행함
제 4 강의. 스택과큐자료구조 1 제 4 강. 스택과큐자료구조 학습목차 1. 스택과큐자료구조 2. 스택자료구조 3. 큐자료구조 4. 원형큐의구현 2 1. 스택 (Stack) 과큐자료구조 리스트, 스택과큐 (Stack and Queue) 스택과큐는리스트자료구조의특별한경우이다. 리스트 - 순서가있다 - 읽기, 삽입 (insert) 과삭제 (delete) 를리스트의어느곳에서나행함
q 이장에서다룰내용 1 연결자료구조방식 2 단순연결리스트 3 원형연결리스트 4 이중연결리스트 3 다항식의연결자료구조표현 2
 연결자료구조표현방식 IT CookBook, 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조 q 이장에서다룰내용 1 연결자료구조방식 2 단순연결리스트 3 원형연결리스트 4 이중연결리스트 3 다항식의연결자료구조표현 2 q 연결자료구조 v 순차자료구조의문제점 삽입연산이나삭제연산후에연속적인물리주소를유지하기위해서원소들을이동시키는추가적인작업과시간소요 Ø 원소들의이동작업으로인한오버헤드는원소의개수가많고삽입
연결자료구조표현방식 IT CookBook, 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조 q 이장에서다룰내용 1 연결자료구조방식 2 단순연결리스트 3 원형연결리스트 4 이중연결리스트 3 다항식의연결자료구조표현 2 q 연결자료구조 v 순차자료구조의문제점 삽입연산이나삭제연산후에연속적인물리주소를유지하기위해서원소들을이동시키는추가적인작업과시간소요 Ø 원소들의이동작업으로인한오버헤드는원소의개수가많고삽입
Microsoft PowerPoint - ch09 - 연결형리스트, Stack, Queue와 응용 pm0100
 2015-1 프로그래밍언어 9. 연결형리스트, Stack, Queue 2015 년 5 월 4 일 교수김영탁 영남대학교공과대학정보통신공학과 (Tel : +82-53-810-2497; Fax : +82-53-810-4742 http://antl.yu.ac.kr/; E-mail : ytkim@yu.ac.kr) 연결리스트 (Linked List) 연결리스트연산 Stack
2015-1 프로그래밍언어 9. 연결형리스트, Stack, Queue 2015 년 5 월 4 일 교수김영탁 영남대학교공과대학정보통신공학과 (Tel : +82-53-810-2497; Fax : +82-53-810-4742 http://antl.yu.ac.kr/; E-mail : ytkim@yu.ac.kr) 연결리스트 (Linked List) 연결리스트연산 Stack
슬라이드 1
 6-1 리스트 (list) 란순서를가진항목들을표현하는자료구조 리스트를구현하는두가지방법 배열 (array) 을이용하는방법 구현간단 삽입, 삭제시오버헤드 항목의개수제한 연결리스트 (linked list) 를이용하는방법 구현복잡 삽입, 삭제가효율적 크기가제한되지않음 6-2 객체 : n 개의 element 형으로구성된순서있는모임 연산 : add_last(list,
6-1 리스트 (list) 란순서를가진항목들을표현하는자료구조 리스트를구현하는두가지방법 배열 (array) 을이용하는방법 구현간단 삽입, 삭제시오버헤드 항목의개수제한 연결리스트 (linked list) 를이용하는방법 구현복잡 삽입, 삭제가효율적 크기가제한되지않음 6-2 객체 : n 개의 element 형으로구성된순서있는모임 연산 : add_last(list,
<4D F736F F F696E74202D FBFACB0E120C0DAB7E1B1B8C1B6205BC8A3C8AF20B8F0B5E55D>
 연결자료구조 IT CookBook, C 로배우는쉬운자료구조 ( 개정판 ) Contents 학습목표 연결자료구조를이해한다. 순차자료구조와연결자료구조의차이와장단점을알아본다. 연결리스트의종류와특징을알아본다. 연결자료구조를이용한다항식의덧셈연산방법을알아본다. 내용 배열연결자료구조를이해한다. 순차자료구조와연결자료구조의차이와장단점을알아본다. 연결리스트의종류와특징을알아본다.
연결자료구조 IT CookBook, C 로배우는쉬운자료구조 ( 개정판 ) Contents 학습목표 연결자료구조를이해한다. 순차자료구조와연결자료구조의차이와장단점을알아본다. 연결리스트의종류와특징을알아본다. 연결자료구조를이용한다항식의덧셈연산방법을알아본다. 내용 배열연결자료구조를이해한다. 순차자료구조와연결자료구조의차이와장단점을알아본다. 연결리스트의종류와특징을알아본다.
A Hierarchical Approach to Interactive Motion Editing for Human-like Figures
 단일연결리스트 (Singly Linked List) 신찬수 연결리스트 (linked list)? tail 서울부산수원용인 null item next 구조체복습 struct name_card { char name[20]; int date; } struct name_card a; // 구조체변수 a 선언 a.name 또는 a.date // 구조체 a의멤버접근 struct
단일연결리스트 (Singly Linked List) 신찬수 연결리스트 (linked list)? tail 서울부산수원용인 null item next 구조체복습 struct name_card { char name[20]; int date; } struct name_card a; // 구조체변수 a 선언 a.name 또는 a.date // 구조체 a의멤버접근 struct
chap 5: Trees
 5. Threaded Binary Tree 기본개념 n 개의노드를갖는이진트리에는 2n 개의링크가존재 2n 개의링크중에 n + 1 개의링크값은 null Null 링크를다른노드에대한포인터로대체 Threads Thread 의이용 ptr left_child = NULL 일경우, ptr left_child 를 ptr 의 inorder predecessor 를가리키도록변경
5. Threaded Binary Tree 기본개념 n 개의노드를갖는이진트리에는 2n 개의링크가존재 2n 개의링크중에 n + 1 개의링크값은 null Null 링크를다른노드에대한포인터로대체 Threads Thread 의이용 ptr left_child = NULL 일경우, ptr left_child 를 ptr 의 inorder predecessor 를가리키도록변경
Chapter 4. LISTS
 연결리스트의응용 류관희 충북대학교 1 체인연산 체인을역순으로만드는 (inverting) 연산 3 개의포인터를적절히이용하여제자리 (in place) 에서문제를해결 typedef struct listnode *listpointer; typedef struct listnode { char data; listpointer link; ; 2 체인연산 체인을역순으로만드는
연결리스트의응용 류관희 충북대학교 1 체인연산 체인을역순으로만드는 (inverting) 연산 3 개의포인터를적절히이용하여제자리 (in place) 에서문제를해결 typedef struct listnode *listpointer; typedef struct listnode { char data; listpointer link; ; 2 체인연산 체인을역순으로만드는
<4D F736F F F696E74202D20C1A637C0E52DB0EDB1DEBFACB0E1B8AEBDBAC6AE2E >
 제 7 강의. 고급연결리스트 1. 원형연결리스트 2. 이중연결리스트 3. 연결리스트알고리즘 1 1. 원형연결리스트 (Circularly Linked Lists) 원형연결리스트란? 연결리스트의맨끝노드를첫번째노드와연결시켜서원형으로만든리스트 단순연결리스트 (Singly Linked List) 불편한점 - 연결리스트의노드포인터를알고있을때첫번째노드는바로찾아갈수있지만마지막노드는리스트전체를따라가면서끝을찾아가야한다
제 7 강의. 고급연결리스트 1. 원형연결리스트 2. 이중연결리스트 3. 연결리스트알고리즘 1 1. 원형연결리스트 (Circularly Linked Lists) 원형연결리스트란? 연결리스트의맨끝노드를첫번째노드와연결시켜서원형으로만든리스트 단순연결리스트 (Singly Linked List) 불편한점 - 연결리스트의노드포인터를알고있을때첫번째노드는바로찾아갈수있지만마지막노드는리스트전체를따라가면서끝을찾아가야한다
11장 포인터
 Dynamic Memory and Linked List 1 동적할당메모리의개념 프로그램이메모리를할당받는방법 정적 (static) 동적 (dynamic) 정적메모리할당 프로그램이시작되기전에미리정해진크기의메모리를할당받는것 메모리의크기는프로그램이시작하기전에결정 int i, j; int buffer[80]; char name[] = data structure"; 처음에결정된크기보다더큰입력이들어온다면처리하지못함
Dynamic Memory and Linked List 1 동적할당메모리의개념 프로그램이메모리를할당받는방법 정적 (static) 동적 (dynamic) 정적메모리할당 프로그램이시작되기전에미리정해진크기의메모리를할당받는것 메모리의크기는프로그램이시작하기전에결정 int i, j; int buffer[80]; char name[] = data structure"; 처음에결정된크기보다더큰입력이들어온다면처리하지못함
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 스택, 큐 7 장. 큐 리스트작업은시간과무관하게정의스택과큐의작업은시간을기준으로정의큐는가장먼저삽입된데이터가먼저삭제되는특성의자료형을추상화 학습목표 추상자료형큐의기본개념을스택과대조하여이해한다. 추상자료형큐를구현하기위한세가지방법을이해한다. 원형배열이필요한이유와동작원리를이해한다. 큐의응용예를구체적으로명확하게이해한다. 1 Section 01 큐개념 - 큐 큐 = 대기열
스택, 큐 7 장. 큐 리스트작업은시간과무관하게정의스택과큐의작업은시간을기준으로정의큐는가장먼저삽입된데이터가먼저삭제되는특성의자료형을추상화 학습목표 추상자료형큐의기본개념을스택과대조하여이해한다. 추상자료형큐를구현하기위한세가지방법을이해한다. 원형배열이필요한이유와동작원리를이해한다. 큐의응용예를구체적으로명확하게이해한다. 1 Section 01 큐개념 - 큐 큐 = 대기열
Chapter 4. LISTS
 6. 동치관계 (Equivalence Relations) 동치관계 reflexive, symmetric, transitive 성질을만족 "equal to"(=) 관계는동치관계임. x = x x = y 이면 y = x x = y 이고 y = z 이면 x = z 동치관계를이용하여집합 S 를 동치클래스 로분할 동일한클래스내의원소 x, y 에대해서는 x y 관계성립
6. 동치관계 (Equivalence Relations) 동치관계 reflexive, symmetric, transitive 성질을만족 "equal to"(=) 관계는동치관계임. x = x x = y 이면 y = x x = y 이고 y = z 이면 x = z 동치관계를이용하여집합 S 를 동치클래스 로분할 동일한클래스내의원소 x, y 에대해서는 x y 관계성립
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 7 장. 큐 스택, 큐 리스트작업은시간과무관하게정의 스택과큐의작업은시간을기준으로정의 큐는가장먼저삽입된데이터가먼저삭제되는특성의자료형을추상화 학습목표 추상자료형큐의기본개념을스택과대조하여이해한다. 추상자료형큐를구현하기위한세가지방법을이해한다. 원형배열이필요한이유와동작원리를이해한다. 큐의응용예를구체적으로명확하게이해한다. 1 큐 큐 = 대기열 2 큐 대기열을모델링 선입선출,
7 장. 큐 스택, 큐 리스트작업은시간과무관하게정의 스택과큐의작업은시간을기준으로정의 큐는가장먼저삽입된데이터가먼저삭제되는특성의자료형을추상화 학습목표 추상자료형큐의기본개념을스택과대조하여이해한다. 추상자료형큐를구현하기위한세가지방법을이해한다. 원형배열이필요한이유와동작원리를이해한다. 큐의응용예를구체적으로명확하게이해한다. 1 큐 큐 = 대기열 2 큐 대기열을모델링 선입선출,
리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L = n ( item0, item1,..., item -1) l 리스트의예 l 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) l 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ
 00. 리스트 자료구조 01. 링크드 리스트 02. 더블 링크드 리스트 03. 환형 링크드 리스트 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L = n ( item0, item1,..., item -1) l 리스트의예 l 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) l 한글자음의모임 : (
00. 리스트 자료구조 01. 링크드 리스트 02. 더블 링크드 리스트 03. 환형 링크드 리스트 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L = n ( item0, item1,..., item -1) l 리스트의예 l 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) l 한글자음의모임 : (
1장. 리스트
 01. 링크드리스트 02. 더블링크드리스트 03. 환형링크드리스트 배열과는달리유연하게크기를바꿀수있는자료구조 각노드는다음노드를가리키는포인터를가짐. 각노드를다음노드를가리키는포인터로연결하여만든리스트. Single Linked List 라고도함. 링크드리스트의첫번째노드를헤드 (Head), 마지막노드를테일 (Tail) 이라고한다. C 언어로표현하는링크드리스트의노드 typedef
01. 링크드리스트 02. 더블링크드리스트 03. 환형링크드리스트 배열과는달리유연하게크기를바꿀수있는자료구조 각노드는다음노드를가리키는포인터를가짐. 각노드를다음노드를가리키는포인터로연결하여만든리스트. Single Linked List 라고도함. 링크드리스트의첫번째노드를헤드 (Head), 마지막노드를테일 (Tail) 이라고한다. C 언어로표현하는링크드리스트의노드 typedef
<4D F736F F F696E74202D20C0DAB7E1B1B8C1B65FC3E2BCAEBCF6BEF7>
 한국방송통신대학교컴퓨터과학과 2 학년자료구조 제 1 장기본개념 자료와정보 3 알고리즘 4 자료 data : 현실세계에서관찰이나측정을통해수집된값 value 이나사실 fact 특정한일을수행하는명령어들의유한집합 정보 information : 자료를처리 / 추출 process 해서얻어진유용한결과 입 출 력 : 외부에서제공되는자료가있을수있다력 : 적어도한가지결과를생성한다
한국방송통신대학교컴퓨터과학과 2 학년자료구조 제 1 장기본개념 자료와정보 3 알고리즘 4 자료 data : 현실세계에서관찰이나측정을통해수집된값 value 이나사실 fact 특정한일을수행하는명령어들의유한집합 정보 information : 자료를처리 / 추출 process 해서얻어진유용한결과 입 출 력 : 외부에서제공되는자료가있을수있다력 : 적어도한가지결과를생성한다
C 언어 강의노트
 C언어 (CSE2035) (15-1 Lists) Linear list 의구성, Insertion, deletion 윤용운, Ph.D. Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Sogang University Seoul, Korea Tel: 010-3204-6811 Email : yuyoon0@sogang.ac.kr 2018-01-11
C언어 (CSE2035) (15-1 Lists) Linear list 의구성, Insertion, deletion 윤용운, Ph.D. Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Sogang University Seoul, Korea Tel: 010-3204-6811 Email : yuyoon0@sogang.ac.kr 2018-01-11
Lab 3. 실습문제 (Single linked list)_해답.hwp
 Lab 3. Singly-linked list 의구현 실험실습일시 : 2009. 3. 30. 담당교수 : 정진우 담당조교 : 곽문상 보고서제출기한 : 2009. 4. 5. 학과 : 학번 : 성명 : 실습과제목적 : 이론시간에배운 Singly-linked list를실제로구현할수있다. 실습과제내용 : 주어진소스를이용해 Singly-linked list의각함수를구현한다.
Lab 3. Singly-linked list 의구현 실험실습일시 : 2009. 3. 30. 담당교수 : 정진우 담당조교 : 곽문상 보고서제출기한 : 2009. 4. 5. 학과 : 학번 : 성명 : 실습과제목적 : 이론시간에배운 Singly-linked list를실제로구현할수있다. 실습과제내용 : 주어진소스를이용해 Singly-linked list의각함수를구현한다.
이번장에서학습할내용 동적메모리란? malloc() 와 calloc() 연결리스트 파일을이용하면보다많은데이터를유용하고지속적으로사용및관리할수있습니다. 2
 제 17 장동적메모리와연결리스트 유준범 (JUNBEOM YOO) Ver. 2.0 jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr 본강의자료는생능출판사의 PPT 강의자료 를기반으로제작되었습니다. 이번장에서학습할내용 동적메모리란? malloc() 와 calloc() 연결리스트 파일을이용하면보다많은데이터를유용하고지속적으로사용및관리할수있습니다.
제 17 장동적메모리와연결리스트 유준범 (JUNBEOM YOO) Ver. 2.0 jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr 본강의자료는생능출판사의 PPT 강의자료 를기반으로제작되었습니다. 이번장에서학습할내용 동적메모리란? malloc() 와 calloc() 연결리스트 파일을이용하면보다많은데이터를유용하고지속적으로사용및관리할수있습니다.
Lab 4. 실습문제 (Circular singly linked list)_해답.hwp
 Lab 4. Circular singly-linked list 의구현 실험실습일시 : 2009. 4. 6. 담당교수 : 정진우 담당조교 : 곽문상 보고서제출기한 : 2009. 4. 12. 학과 : 학번 : 성명 : 실습과제목적 : 이론시간에배운 Circular Singly-linked list를실제로구현할수있다. 실습과제내용 : 주어진소스를이용해 Circular
Lab 4. Circular singly-linked list 의구현 실험실습일시 : 2009. 4. 6. 담당교수 : 정진우 담당조교 : 곽문상 보고서제출기한 : 2009. 4. 12. 학과 : 학번 : 성명 : 실습과제목적 : 이론시간에배운 Circular Singly-linked list를실제로구현할수있다. 실습과제내용 : 주어진소스를이용해 Circular
Microsoft PowerPoint - ch07 - 포인터 pm0415
 2015-1 프로그래밍언어 7. 포인터 (Pointer), 동적메모리할당 2015 년 4 월 4 일 교수김영탁 영남대학교공과대학정보통신공학과 (Tel : +82-53-810-2497; Fax : +82-53-810-4742 http://antl.yu.ac.kr/; E-mail : ytkim@yu.ac.kr) Outline 포인터 (pointer) 란? 간접참조연산자
2015-1 프로그래밍언어 7. 포인터 (Pointer), 동적메모리할당 2015 년 4 월 4 일 교수김영탁 영남대학교공과대학정보통신공학과 (Tel : +82-53-810-2497; Fax : +82-53-810-4742 http://antl.yu.ac.kr/; E-mail : ytkim@yu.ac.kr) Outline 포인터 (pointer) 란? 간접참조연산자
원형연결리스트에대한설명중틀린것은 모든노드들이연결되어있다 마지막에삽입하기가간단한다 헤더노드를가질수있다 최종노드포인터가 NULL이다 리스트의 번째요소를가장빠르게찾을수있는구현방법은무엇인가 배열 단순연결리스트 원형연결리스트 이중연결리스트 단순연결리스트의노드포인터 가마지막노드를
 리스트에대한설명중틀린것은 구조체도리스트의요소가될수있다 리스트의요소간에는순서가있다 리스트는여러가지방법으로구현될수있다 리스트는집합과동일하다 다음은순차적표현과연결된표현을비교한것이다 설명이틀린것은 연결된표현은포인터를가지고있어상대적으로크기가작아진다 연결된표현은삽입이용이하다 순차적표현은연결된표현보다액세스시간이많이걸린다 연결된표현으로작성된리스트를 개로분리하기가쉽다 다음은연결리스트에서있을수있는여러가지경우를설명했는데잘못된항목은
리스트에대한설명중틀린것은 구조체도리스트의요소가될수있다 리스트의요소간에는순서가있다 리스트는여러가지방법으로구현될수있다 리스트는집합과동일하다 다음은순차적표현과연결된표현을비교한것이다 설명이틀린것은 연결된표현은포인터를가지고있어상대적으로크기가작아진다 연결된표현은삽입이용이하다 순차적표현은연결된표현보다액세스시간이많이걸린다 연결된표현으로작성된리스트를 개로분리하기가쉽다 다음은연결리스트에서있을수있는여러가지경우를설명했는데잘못된항목은
<443A5C4C C4B48555C B3E25C32C7D0B1E25CBCB3B0E8C7C1B7CEC1A7C6AE425CBED0C3E0C7C1B7CEB1D7B7A55C4C656D70656C2D5A69762E637070>
 /* */ /* LZWIN.C : Lempel-Ziv compression using Sliding Window */ /* */ #include "stdafx.h" #include "Lempel-Ziv.h" 1 /* 큐를초기화 */ void LZ::init_queue(void) front = rear = 0; /* 큐가꽉찼으면 1 을되돌림 */ int LZ::queue_full(void)
/* */ /* LZWIN.C : Lempel-Ziv compression using Sliding Window */ /* */ #include "stdafx.h" #include "Lempel-Ziv.h" 1 /* 큐를초기화 */ void LZ::init_queue(void) front = rear = 0; /* 큐가꽉찼으면 1 을되돌림 */ int LZ::queue_full(void)
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 System Software Experiment 1 Lecture 5 - Array Spring 2019 Hwansoo Han (hhan@skku.edu) Advanced Research on Compilers and Systems, ARCS LAB Sungkyunkwan University http://arcs.skku.edu/ 1 배열 (Array) 동일한타입의데이터가여러개저장되어있는저장장소
System Software Experiment 1 Lecture 5 - Array Spring 2019 Hwansoo Han (hhan@skku.edu) Advanced Research on Compilers and Systems, ARCS LAB Sungkyunkwan University http://arcs.skku.edu/ 1 배열 (Array) 동일한타입의데이터가여러개저장되어있는저장장소
1. 리스트개념 리스트 (list) 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : (ᄀ,ᄂ,,ᄒ
 Linked List 2010 2 학기 SANGJI University 1. 리스트개념 리스트 (list) 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : (ᄀ,ᄂ,,ᄒ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
Linked List 2010 2 학기 SANGJI University 1. 리스트개념 리스트 (list) 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : (ᄀ,ᄂ,,ᄒ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
리스트구현방법 배열 (array) 을이용하는방법 구현이간단 삽입, 삭제동작에따른원소이동. 항목의개수제한, 정적기억공간할당. 메모리낭비, 오버플로우 연결리스트 (linked list) 를이용하는방법 구현이복잡 삽입, 삭제가효율적 크기가제한되지않음 Lecture 03_Li
 Linked List 2011 2 학기 SANGJI University 리스트 (list) 1. 리스트개념 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : (ᄀ,ᄂ,,ᄒ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
Linked List 2011 2 학기 SANGJI University 리스트 (list) 1. 리스트개념 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : (ᄀ,ᄂ,,ᄒ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
4장. 순차자료구조
 순차자료구조방식 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조 이장에서다룰내용 1 선형리스트 2 선형리스트의구현 3 다항식의순차자료구조표현 4 행렬의순차자료구조표현 2 선형리스트 (1) 리스트 (List) 자료를나열한목록 ( 집합 ) 리스트의예 3 선형리스트 (2) 선형리스트 (Linear List) 순서리스트 (Ordered List) 자료들간에순서를갖는리스트 선형리스트의예 4
순차자료구조방식 자바로배우는쉬운자료구조 이장에서다룰내용 1 선형리스트 2 선형리스트의구현 3 다항식의순차자료구조표현 4 행렬의순차자료구조표현 2 선형리스트 (1) 리스트 (List) 자료를나열한목록 ( 집합 ) 리스트의예 3 선형리스트 (2) 선형리스트 (Linear List) 순서리스트 (Ordered List) 자료들간에순서를갖는리스트 선형리스트의예 4
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 4: 리스트 C 로쉽게풀어쓴자료구조 생능출판사 2005 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item0, item1,..., itemn 1) 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 : (Ace, 2,3,,King)
CHAP 4: 리스트 C 로쉽게풀어쓴자료구조 생능출판사 2005 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item0, item1,..., itemn 1) 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 : (Ace, 2,3,,King)
Microsoft PowerPoint - chap4_list
 Chap. 4 : 리스트 (list) 2007 학년도 2 학기 리스트 1. 리스트개념 ~ 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 ~ 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 ~ 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) ~ 한글자음의모임 : (ᆨ,ᆫ,,ᄒ) ~ 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
Chap. 4 : 리스트 (list) 2007 학년도 2 학기 리스트 1. 리스트개념 ~ 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 ~ 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 ~ 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) ~ 한글자음의모임 : (ᆨ,ᆫ,,ᄒ) ~ 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
슬라이드 1
 Data Structure Chapter 4. 리스트 Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University dqkim@hanyang.ac.kr 리스트추상데이터타입 리스트 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 :
Data Structure Chapter 4. 리스트 Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University dqkim@hanyang.ac.kr 리스트추상데이터타입 리스트 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 :
4장
 CHAP 4: 리스트 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item 0, item 1,..., item n 1) 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 영어알파벳 : (a, b,,z) 카드 : (Ace, 2,3,,King) 쇼핑리스트 리스트의연산 새로운항목을리스트의끝,
CHAP 4: 리스트 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item 0, item 1,..., item n 1) 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 영어알파벳 : (a, b,,z) 카드 : (Ace, 2,3,,King) 쇼핑리스트 리스트의연산 새로운항목을리스트의끝,
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 제 2 장연결리스트 리스트 일반적인리스트 (List) 는일련의동일한타입의항목 (item) 들 실생활의예 : 학생명단, 시험성적, 서점의신간서적, 상점의판매품목, 실시간급상승검색어, 버킷리스트등 일반적인리스트의구현 : - 1 차원파이썬리스트 (list) - 단순연결리스트 - 이중연결리스트 - 원형연결리스트 2.1 단순연결리스트 단순연결리스트 (Singly Linked
제 2 장연결리스트 리스트 일반적인리스트 (List) 는일련의동일한타입의항목 (item) 들 실생활의예 : 학생명단, 시험성적, 서점의신간서적, 상점의판매품목, 실시간급상승검색어, 버킷리스트등 일반적인리스트의구현 : - 1 차원파이썬리스트 (list) - 단순연결리스트 - 이중연결리스트 - 원형연결리스트 2.1 단순연결리스트 단순연결리스트 (Singly Linked
리스트연산, 검색 + 삽입 + 삭제 새로운항목을리스트의처음, 중간, 끝에추가. 기존의항목을리스트의임의의위치에서삭제. 모든항목을삭제. 기존항목을대치 (replace). 리스트가특정항목을가지고있는지를검색 (search). 리스트의특정위치의항목을반환. 리스트안의항목의개수를센
 Linked List 2014 2 학기 SANGJI University 리스트 (list) 1. 리스트개념 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
Linked List 2014 2 학기 SANGJI University 리스트 (list) 1. 리스트개념 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
슬라이드 1
 Linked List 2015 2 학기 SANGJI University 1. 리스트개념 리스트 (list) 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
Linked List 2015 2 학기 SANGJI University 1. 리스트개념 리스트 (list) 고정된길이의자료 ( 원소 ) 들을순차적으로나열해놓은집합을가르키는자료구조의추상적인개념 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 (set) : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트
Microsoft PowerPoint 자바-기본문법(Ch2).pptx
 자바기본문법 1. 기본사항 2. 자료형 3. 변수와상수 4. 연산자 1 주석 (Comments) 이해를돕기위한설명문 종류 // /* */ /** */ 활용예 javadoc HelloApplication.java 2 주석 (Comments) /* File name: HelloApplication.java Created by: Jung Created on: March
자바기본문법 1. 기본사항 2. 자료형 3. 변수와상수 4. 연산자 1 주석 (Comments) 이해를돕기위한설명문 종류 // /* */ /** */ 활용예 javadoc HelloApplication.java 2 주석 (Comments) /* File name: HelloApplication.java Created by: Jung Created on: March
Microsoft PowerPoint - 06-List.ppt
 Chapter 4. 리스트 (List) Today.. 리스트의개념과추상데이터타입 리스트구현방법 배열 (Array) vs. 연결리스트 (Linked List) 2 1 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L = n ( item 0, item 1,..., item 1 ) 리스트의예
Chapter 4. 리스트 (List) Today.. 리스트의개념과추상데이터타입 리스트구현방법 배열 (Array) vs. 연결리스트 (Linked List) 2 1 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L = n ( item 0, item 1,..., item 1 ) 리스트의예
중간고사 (자료 구조)
 Data Structures 215 중간고사 문제에서명시적으로기술하지않은부분은교재의내용에근거함. 215. 1. 27. 1 다음용어에대하여간단하게설명하시오 ( 각 3 점 *1=3 점 ) 1 abstract data type 6 Circular linked list 2 recursion 3 time complexity 4 space complexity 5 Single
Data Structures 215 중간고사 문제에서명시적으로기술하지않은부분은교재의내용에근거함. 215. 1. 27. 1 다음용어에대하여간단하게설명하시오 ( 각 3 점 *1=3 점 ) 1 abstract data type 6 Circular linked list 2 recursion 3 time complexity 4 space complexity 5 Single
03장.스택.key
 ---------------- DATA STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- 03CHAPTER 1 ? (stack): (LIFO:Last-In First-Out) 2 : top : ( index -1 ),,, 3 : ( ) ( ) -> ->. ->.... 4 Stack ADT : (LIFO) : init():. is_empty():
---------------- DATA STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- 03CHAPTER 1 ? (stack): (LIFO:Last-In First-Out) 2 : top : ( index -1 ),,, 3 : ( ) ( ) -> ->. ->.... 4 Stack ADT : (LIFO) : init():. is_empty():
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 4 : 리스트 조영임 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item0, item1,..., itemn 1) 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 : (Ace,
CHAP 4 : 리스트 조영임 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item0, item1,..., itemn 1) 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 : (Ace,
chap01_time_complexity.key
 1 : (resource),,, 2 (time complexity),,, (worst-case analysis) (average-case analysis) 3 (Asymptotic) n growth rate Θ-, Ο- ( ) 4 : n data, n/2. int sample( int data[], int n ) { int k = n/2 ; return data[k]
1 : (resource),,, 2 (time complexity),,, (worst-case analysis) (average-case analysis) 3 (Asymptotic) n growth rate Θ-, Ο- ( ) 4 : n data, n/2. int sample( int data[], int n ) { int k = n/2 ; return data[k]
슬라이드 1
 자료구조 (Data Structures), 4 장. 리스트 담당교수 : 조미경 이번장에서학습할내용 * 리스트란? * 배열로리스트구현 * 연결리스트로리스트구현 * 연결리스트종류 * 연결리스트응용 : 다항식구현 2/63 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item 0,
자료구조 (Data Structures), 4 장. 리스트 담당교수 : 조미경 이번장에서학습할내용 * 리스트란? * 배열로리스트구현 * 연결리스트로리스트구현 * 연결리스트종류 * 연결리스트응용 : 다항식구현 2/63 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 L ( item 0,
chap x: G입력
 원형큐 (Circular Queue) [2] [3] [2] [3] [1] [4] [1] [4] [0] [5] front = 0, rear = 0 [2] [3] [0] [5] front = 0, rear = 3 [1] [4] [0] [5] front = 0, rear = 0 최대큐이용률 = MAX_Q_SIZE 1 3 장. 스택과큐 (Page 13) 원형큐의구현
원형큐 (Circular Queue) [2] [3] [2] [3] [1] [4] [1] [4] [0] [5] front = 0, rear = 0 [2] [3] [0] [5] front = 0, rear = 3 [1] [4] [0] [5] front = 0, rear = 0 최대큐이용률 = MAX_Q_SIZE 1 3 장. 스택과큐 (Page 13) 원형큐의구현
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 5 : 스택 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 5.1 스택추상데이터타입 스택 (stack) 이란?: 쌓아놓은더미 2 스택의특징 후입선출 (LIFO:Last-In First-Out): 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감. D C B C B C B C B A A A A 3 스택의구조 요소 (element) 스택에저장되는것 C 스택상단 (top) : 스택에서입출력이이루어지는부분
CHAP 5 : 스택 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 5.1 스택추상데이터타입 스택 (stack) 이란?: 쌓아놓은더미 2 스택의특징 후입선출 (LIFO:Last-In First-Out): 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감. D C B C B C B C B A A A A 3 스택의구조 요소 (element) 스택에저장되는것 C 스택상단 (top) : 스택에서입출력이이루어지는부분
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 4: 리스트 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 : (Ace, 2,3,,King) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트 L ( item0, item1,..., itemn 1) 리스트의연산
CHAP 4: 리스트 리스트란? 리스트 (list), 선형리스트 (linear list): 순서를가진항목들의모임 집합 : 항목간의순서의개념이없음 리스트의예 요일 : ( 일요일, 월요일,, 토요일 ) 한글자음의모임 : ( ㄱ, ㄴ,, ㅎ ) 카드 : (Ace, 2,3,,King) 핸드폰의문자메시지리스트 L ( item0, item1,..., itemn 1) 리스트의연산
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 @ Lesson 2... ( ). ( ). @ vs. logic data method variable behavior attribute method field Flow (Type), ( ) member @ () : C program Method A ( ) Method B ( ) Method C () program : Java, C++, C# data @ Program
@ Lesson 2... ( ). ( ). @ vs. logic data method variable behavior attribute method field Flow (Type), ( ) member @ () : C program Method A ( ) Method B ( ) Method C () program : Java, C++, C# data @ Program
Microsoft PowerPoint - 자료구조2008Chap06
 제 6 장연결리스트 연결리스트개요 2 일정한순서를가지는데이터요소들을표현하는방법중의하나이다. 배열과다르게데이터요소들의논리적인순서만유지되고기억장소내에서는각데이터요소들은논리적인순서와는상관없는임의의위치를가지도록하는자료구조이다. 연결리스트에서는각데이터요소들이기억장소내의어떤위치에어떤항목이있는지를표시해주어야한다. 이를위해데이터요소에는데이터값 (value) 뿐만아니라위치정보
제 6 장연결리스트 연결리스트개요 2 일정한순서를가지는데이터요소들을표현하는방법중의하나이다. 배열과다르게데이터요소들의논리적인순서만유지되고기억장소내에서는각데이터요소들은논리적인순서와는상관없는임의의위치를가지도록하는자료구조이다. 연결리스트에서는각데이터요소들이기억장소내의어떤위치에어떤항목이있는지를표시해주어야한다. 이를위해데이터요소에는데이터값 (value) 뿐만아니라위치정보
데이터구조 (Chapter 3: Stacks and Queues) 2011 년봄학기 숙명여자대학교이과대학멀티미디어과학과박영호
 데이터구조 (Chapter 3: Stacks and Queues) 2011 년봄학기 숙명여자대학교이과대학멀티미디어과학과박영호 Index Chapter 01: Basic Concepts Chapter 02: Arrays and Structures Chapter 03: Stacks and Queues Chapter 04: Lists Chapter 05: Trees
데이터구조 (Chapter 3: Stacks and Queues) 2011 년봄학기 숙명여자대학교이과대학멀티미디어과학과박영호 Index Chapter 01: Basic Concepts Chapter 02: Arrays and Structures Chapter 03: Stacks and Queues Chapter 04: Lists Chapter 05: Trees
Chap 6: Graphs
 그래프표현법 인접행렬 (Adjacency Matrix) 인접리스트 (Adjacency List) 인접다중리스트 (Adjacency Multilist) 6 장. 그래프 (Page ) 인접행렬 (Adjacency Matrix) n 개의 vertex 를갖는그래프 G 의인접행렬의구성 A[n][n] (u, v) E(G) 이면, A[u][v] = Otherwise, A[u][v]
그래프표현법 인접행렬 (Adjacency Matrix) 인접리스트 (Adjacency List) 인접다중리스트 (Adjacency Multilist) 6 장. 그래프 (Page ) 인접행렬 (Adjacency Matrix) n 개의 vertex 를갖는그래프 G 의인접행렬의구성 A[n][n] (u, v) E(G) 이면, A[u][v] = Otherwise, A[u][v]
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 @ Lesson 3 if, if else, if else if, switch case for, while, do while break, continue : System.in, args, JOptionPane for (,, ) @ vs. logic data method variable Data Data Flow (Type), ( ) @ Member field
@ Lesson 3 if, if else, if else if, switch case for, while, do while break, continue : System.in, args, JOptionPane for (,, ) @ vs. logic data method variable Data Data Flow (Type), ( ) @ Member field
Microsoft PowerPoint - logo_3.ppt [호환 모드]
![Microsoft PowerPoint - logo_3.ppt [호환 모드] Microsoft PowerPoint - logo_3.ppt [호환 모드]](/thumbs/96/130256621.jpg) Logo Programming 학습목표 데이터종류를의미하는데이터타입에대해살펴본다. (LOGO의데이터타입 : 단어, 리스트, 배열 ) 값을저장하는공간인변수에대해살펴본다. 데이터관리하기에대해살펴본다. 2012. 5. 박남제 namjepark@jejunu.ac.kr < 데이터타입 > - 단어 단어단어 (word) 는 1 개이상의문자들을나열한것, 123 같은수도단어
Logo Programming 학습목표 데이터종류를의미하는데이터타입에대해살펴본다. (LOGO의데이터타입 : 단어, 리스트, 배열 ) 값을저장하는공간인변수에대해살펴본다. 데이터관리하기에대해살펴본다. 2012. 5. 박남제 namjepark@jejunu.ac.kr < 데이터타입 > - 단어 단어단어 (word) 는 1 개이상의문자들을나열한것, 123 같은수도단어
학습목차 2.1 다차원배열이란 차원배열의주소와값의참조
 - Part2- 제 2 장다차원배열이란무엇인가 학습목차 2.1 다차원배열이란 2. 2 2 차원배열의주소와값의참조 2.1 다차원배열이란 2.1 다차원배열이란 (1/14) 다차원배열 : 2 차원이상의배열을의미 1 차원배열과다차원배열의비교 1 차원배열 int array [12] 행 2 차원배열 int array [4][3] 행 열 3 차원배열 int array [2][2][3]
- Part2- 제 2 장다차원배열이란무엇인가 학습목차 2.1 다차원배열이란 2. 2 2 차원배열의주소와값의참조 2.1 다차원배열이란 2.1 다차원배열이란 (1/14) 다차원배열 : 2 차원이상의배열을의미 1 차원배열과다차원배열의비교 1 차원배열 int array [12] 행 2 차원배열 int array [4][3] 행 열 3 차원배열 int array [2][2][3]
Microsoft PowerPoint - 07-chap05-Stack.ppt
 / 스택이란? 스택 stack): 쌓아놓은더미 hapter 5 스택 Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr Department of Informatics & Statistics 학습목표 스택의개념이해 스택의동작원리이해 배열과연결리스트를이용한스택구현 스택응용프로그램 스택의특징 후입선출 LIFO:Last-In First-Out) 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감.
/ 스택이란? 스택 stack): 쌓아놓은더미 hapter 5 스택 Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr Department of Informatics & Statistics 학습목표 스택의개념이해 스택의동작원리이해 배열과연결리스트를이용한스택구현 스택응용프로그램 스택의특징 후입선출 LIFO:Last-In First-Out) 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감.
PowerPoint Presentation
 객체지향프로그래밍 클래스, 객체, 메소드 ( 실습 ) 손시운 ssw5176@kangwon.ac.kr 예제 1. 필드만있는클래스 텔레비젼 2 예제 1. 필드만있는클래스 3 예제 2. 여러개의객체생성하기 4 5 예제 3. 메소드가추가된클래스 public class Television { int channel; // 채널번호 int volume; // 볼륨 boolean
객체지향프로그래밍 클래스, 객체, 메소드 ( 실습 ) 손시운 ssw5176@kangwon.ac.kr 예제 1. 필드만있는클래스 텔레비젼 2 예제 1. 필드만있는클래스 3 예제 2. 여러개의객체생성하기 4 5 예제 3. 메소드가추가된클래스 public class Television { int channel; // 채널번호 int volume; // 볼륨 boolean
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 제 3 장. 스택과큐 순서리스트의특별한경우순서리스트 : A=a 0, a 1,, a n-1, n 0 스택 (stack) 톱 (top) 이라고하는한쪽끝에서모든삽입 (push) 과삭제 (pop) 가일어나는순서리스트 스택 S=(a 0,...,a n-1 ): a 0 는 bottom, a n-1 은 top의원소 a i 는원소 a i-1 (0
제 3 장. 스택과큐 순서리스트의특별한경우순서리스트 : A=a 0, a 1,, a n-1, n 0 스택 (stack) 톱 (top) 이라고하는한쪽끝에서모든삽입 (push) 과삭제 (pop) 가일어나는순서리스트 스택 S=(a 0,...,a n-1 ): a 0 는 bottom, a n-1 은 top의원소 a i 는원소 a i-1 (0
슬라이드 1
 Data Structure Chapter 8. 우선순위큐 Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University dqkim@hanyang.ac.kr 우선순위큐추상데이터타입 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue) 정의 : 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게됨 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있음
Data Structure Chapter 8. 우선순위큐 Dong Kyue Kim Hanyang University dqkim@hanyang.ac.kr 우선순위큐추상데이터타입 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue) 정의 : 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게됨 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있음
<BCBCB9CCB3AA20C0DAB7E1202D20BDBAC5C3C5A52E687770>
 스택과큐 (Stack, Queue) 이현환 (NOON) haonun@gmail.com http://noon.tistory.com --------------------------------------------------- - 1 - 목차 --------------------------------------------------- 서론 1. 스택과큐를왜알아야할까?
스택과큐 (Stack, Queue) 이현환 (NOON) haonun@gmail.com http://noon.tistory.com --------------------------------------------------- - 1 - 목차 --------------------------------------------------- 서론 1. 스택과큐를왜알아야할까?
슬라이드 1
 UNIT 6 배열 로봇 SW 교육원 3 기 학습목표 2 배열을사용핛수있다. 배열 3 배열 (Array) 이란? 같은타입 ( 자료형 ) 의여러변수를하나의묶음으로다루는것을배열이라고함 같은타입의많은양의데이터를다룰때효과적임 // 학생 30 명의점수를저장하기위해.. int student_score1; int student_score2; int student_score3;...
UNIT 6 배열 로봇 SW 교육원 3 기 학습목표 2 배열을사용핛수있다. 배열 3 배열 (Array) 이란? 같은타입 ( 자료형 ) 의여러변수를하나의묶음으로다루는것을배열이라고함 같은타입의많은양의데이터를다룰때효과적임 // 학생 30 명의점수를저장하기위해.. int student_score1; int student_score2; int student_score3;...
슬라이드 1
 C programming and Data Structures Overview T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
C programming and Data Structures Overview T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
<4D F736F F F696E74202D20C1A63137C0E520B5BFC0FBB8DEB8F0B8AEBFCD20BFACB0E1B8AEBDBAC6AE>
 쉽게풀어쓴 C 언어 Express 제 17 장동적메모리와연결리스트 이번장에서학습할내용 동적메모리할당의이해 동적메모리할당관련함수 연결리스트 동적메모리할당에대한개념을이해하고응용으로연결리스트를학습합니다. 동적할당메모리의개념 프로그램이메모리를할당받는방법 정적 (static) 동적 (dynamic) 정적메모리할당 정적메모리할당 프로그램이시작되기전에미리정해진크기의메모리를할당받는것
쉽게풀어쓴 C 언어 Express 제 17 장동적메모리와연결리스트 이번장에서학습할내용 동적메모리할당의이해 동적메모리할당관련함수 연결리스트 동적메모리할당에대한개념을이해하고응용으로연결리스트를학습합니다. 동적할당메모리의개념 프로그램이메모리를할당받는방법 정적 (static) 동적 (dynamic) 정적메모리할당 정적메모리할당 프로그램이시작되기전에미리정해진크기의메모리를할당받는것
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 8: 우선순위큐 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue): 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게된다. 가장일반적인큐 : 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있다. 자료구조스택큐우선순위큐 삭제되는요소가장최근에들어온데이터가장먼저들어온데이터가장우선순위가높은데이터
CHAP 8: 우선순위큐 yicho@gachon.ac.kr 1 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue): 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게된다. 가장일반적인큐 : 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있다. 자료구조스택큐우선순위큐 삭제되는요소가장최근에들어온데이터가장먼저들어온데이터가장우선순위가높은데이터
Lab 5. 실습문제 (Double linked list)-1_해답.hwp
 Lab 5. Doubly-linked list 의구현 실험실습일시 : 2009. 4. 13. 담당교수 : 정진우 담당조교 : 곽문상 보고서제출기한 : 2009. 4. 19. 학과 : 학번 : 성명 : 실습과제목적 : 이론시간에배운 Doubly-linked list를실제로구현할수있다. 실습과제내용 : 주어진소스를이용해 Doubly-linked list의각함수를구현한다.
Lab 5. Doubly-linked list 의구현 실험실습일시 : 2009. 4. 13. 담당교수 : 정진우 담당조교 : 곽문상 보고서제출기한 : 2009. 4. 19. 학과 : 학번 : 성명 : 실습과제목적 : 이론시간에배운 Doubly-linked list를실제로구현할수있다. 실습과제내용 : 주어진소스를이용해 Doubly-linked list의각함수를구현한다.
PowerPoint Presentation
 자바프로그래밍 1 배열 손시운 ssw5176@kangwon.ac.kr 배열이필요한이유 예를들어서학생이 10 명이있고성적의평균을계산한다고가정하자. 학생 이 10 명이므로 10 개의변수가필요하다. int s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7, s8, s9; 하지만만약학생이 100 명이라면어떻게해야하는가? int s0, s1, s2, s3, s4,
자바프로그래밍 1 배열 손시운 ssw5176@kangwon.ac.kr 배열이필요한이유 예를들어서학생이 10 명이있고성적의평균을계산한다고가정하자. 학생 이 10 명이므로 10 개의변수가필요하다. int s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7, s8, s9; 하지만만약학생이 100 명이라면어떻게해야하는가? int s0, s1, s2, s3, s4,
PowerPoint Presentation
 Package Class 3 Heeseung Jo 목차 section 1 패키지개요와패키지의사용 section 2 java.lang 패키지의개요 section 3 Object 클래스 section 4 포장 (Wrapper) 클래스 section 5 문자열의개요 section 6 String 클래스 section 7 StringBuffer 클래스 section
Package Class 3 Heeseung Jo 목차 section 1 패키지개요와패키지의사용 section 2 java.lang 패키지의개요 section 3 Object 클래스 section 4 포장 (Wrapper) 클래스 section 5 문자열의개요 section 6 String 클래스 section 7 StringBuffer 클래스 section
제 3 장 스택과 큐
 제 3 장스택과큐 Copyright 2007 DBLAB, Seoul National University 템플릿함수 (1) 클래스와함수의재사용에기여 (1) 템플릿함수를사용하지않는경우 ( 예 ) 정수배열을위한선택정렬함수 SelectionSort( 프로그램 1.6) 부동소수점수의배열을정리하려면? 첫째행에서 int *a를 float *a로변경둘째행에서 정수 를 부동소수점수
제 3 장스택과큐 Copyright 2007 DBLAB, Seoul National University 템플릿함수 (1) 클래스와함수의재사용에기여 (1) 템플릿함수를사용하지않는경우 ( 예 ) 정수배열을위한선택정렬함수 SelectionSort( 프로그램 1.6) 부동소수점수의배열을정리하려면? 첫째행에서 int *a를 float *a로변경둘째행에서 정수 를 부동소수점수
gnu-lee-oop-kor-lec11-1-chap15
 어서와 Java 는처음이지! 제 15 장컬렉션 컬렉션 (collection) 은자바에서자료구조를구현한클래스 자료구조로는리스트 (list), 스택 (stack), 큐 (queue), 집합 (set), 해쉬테이블 (hash table) 등이있다. 자바는컬렉션인터페이스와컬렉션클래스로나누어서제공한다. 자바에서는컬렉션인터페이스를구현한클래스도함께제공하므로이것을간단하게사용할수도있고아니면각자필요에맞추어인터페이스를자신의클래스로구현할수도있다.
어서와 Java 는처음이지! 제 15 장컬렉션 컬렉션 (collection) 은자바에서자료구조를구현한클래스 자료구조로는리스트 (list), 스택 (stack), 큐 (queue), 집합 (set), 해쉬테이블 (hash table) 등이있다. 자바는컬렉션인터페이스와컬렉션클래스로나누어서제공한다. 자바에서는컬렉션인터페이스를구현한클래스도함께제공하므로이것을간단하게사용할수도있고아니면각자필요에맞추어인터페이스를자신의클래스로구현할수도있다.
Microsoft PowerPoint - 제11장 포인터(강의)
 쉽게풀어쓴 C 언어 Express 제 11 장포인터 이번장에서학습할내용 포인터이란? 변수의주소 포인터의선언 간접참조연산자 포인터연산 포인터와배열 포인터와함수 이번장에서는포인터의기초적인지식을학습한다. 포인터란? 포인터 (pointer): 주소를가지고있는변수 1003 1004 1005 영화관 1002 1006 1001 포인터 (pointer) 1007 메모리의구조
쉽게풀어쓴 C 언어 Express 제 11 장포인터 이번장에서학습할내용 포인터이란? 변수의주소 포인터의선언 간접참조연산자 포인터연산 포인터와배열 포인터와함수 이번장에서는포인터의기초적인지식을학습한다. 포인터란? 포인터 (pointer): 주소를가지고있는변수 1003 1004 1005 영화관 1002 1006 1001 포인터 (pointer) 1007 메모리의구조
03장.스택
 ---------------- DT STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- CHPTER 스택 1/30 스택이란? 스택 (stack): 쌓아놓은더미 후입선출 (LIFO:Last-In First-Out) 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감 2/30 스택의구조 스택상단 : top 스택하단 : 불필요 요소, 항목 공백상태, 포화상태 삽입, 삭제연산
---------------- DT STRUCTURES USING C ---------------- CHPTER 스택 1/30 스택이란? 스택 (stack): 쌓아놓은더미 후입선출 (LIFO:Last-In First-Out) 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감 2/30 스택의구조 스택상단 : top 스택하단 : 불필요 요소, 항목 공백상태, 포화상태 삽입, 삭제연산
11장 포인터
 누구나즐기는 C 언어콘서트 제 9 장포인터 이번장에서학습할내용 포인터이란? 변수의주소 포인터의선언 간접참조연산자 포인터연산 포인터와배열 포인터와함수 이번장에서는포인터의기초적인지식을학습한다. 포인터란? 포인터 (pointer): 주소를가지고있는변수 메모리의구조 변수는메모리에저장된다. 메모리는바이트단위로액세스된다. 첫번째바이트의주소는 0, 두번째바이트는 1, 변수와메모리
누구나즐기는 C 언어콘서트 제 9 장포인터 이번장에서학습할내용 포인터이란? 변수의주소 포인터의선언 간접참조연산자 포인터연산 포인터와배열 포인터와함수 이번장에서는포인터의기초적인지식을학습한다. 포인터란? 포인터 (pointer): 주소를가지고있는변수 메모리의구조 변수는메모리에저장된다. 메모리는바이트단위로액세스된다. 첫번째바이트의주소는 0, 두번째바이트는 1, 변수와메모리
설계란 무엇인가?
 금오공과대학교 C++ 프로그래밍 jhhwang@kumoh.ac.kr 컴퓨터공학과 황준하 6 강. 함수와배열, 포인터, 참조목차 함수와포인터 주소값의매개변수전달 주소의반환 함수와배열 배열의매개변수전달 함수와참조 참조에의한매개변수전달 참조의반환 프로그래밍연습 1 /15 6 강. 함수와배열, 포인터, 참조함수와포인터 C++ 매개변수전달방법 값에의한전달 : 변수값,
금오공과대학교 C++ 프로그래밍 jhhwang@kumoh.ac.kr 컴퓨터공학과 황준하 6 강. 함수와배열, 포인터, 참조목차 함수와포인터 주소값의매개변수전달 주소의반환 함수와배열 배열의매개변수전달 함수와참조 참조에의한매개변수전달 참조의반환 프로그래밍연습 1 /15 6 강. 함수와배열, 포인터, 참조함수와포인터 C++ 매개변수전달방법 값에의한전달 : 변수값,
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
 C 언어포인터정복하기 16 강. 포인터로자료구조화하기 TAE-HYONG KIM COMPUTER ENG, KIT 2 학습내용 구조체멤버와구조체포인터멤버 다른구조체 ( 변수 ) 를가리키는구조체 ( 변수 ) 연결된리스트 의구성및관리 포인터로 연결된리스트 탐색하기 3 중첩구조체에자료저장하기 중첩된구조체변수에값저장하기 struct person { char PRID[15];
C 언어포인터정복하기 16 강. 포인터로자료구조화하기 TAE-HYONG KIM COMPUTER ENG, KIT 2 학습내용 구조체멤버와구조체포인터멤버 다른구조체 ( 변수 ) 를가리키는구조체 ( 변수 ) 연결된리스트 의구성및관리 포인터로 연결된리스트 탐색하기 3 중첩구조체에자료저장하기 중첩된구조체변수에값저장하기 struct person { char PRID[15];
JAVA 프로그래밍실습 실습 1) 실습목표 - 메소드개념이해하기 - 매개변수이해하기 - 새메소드만들기 - Math 클래스의기존메소드이용하기 ( ) 문제 - 직사각형모양의땅이있다. 이땅의둘레, 면적과대각
 JAVA 프로그래밍실습 실습 1) 실습목표 - 메소드개념이해하기 - 매개변수이해하기 - 새메소드만들기 - Math 클래스의기존메소드이용하기 ( http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api ) 문제 - 직사각형모양의땅이있다. 이땅의둘레, 면적과대각선의길이를계산하는메소드들을작성하라. 직사각형의가로와세로의길이는주어진다. 대각선의길이는 Math클래스의적절한메소드를이용하여구하라.
JAVA 프로그래밍실습 실습 1) 실습목표 - 메소드개념이해하기 - 매개변수이해하기 - 새메소드만들기 - Math 클래스의기존메소드이용하기 ( http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api ) 문제 - 직사각형모양의땅이있다. 이땅의둘레, 면적과대각선의길이를계산하는메소드들을작성하라. 직사각형의가로와세로의길이는주어진다. 대각선의길이는 Math클래스의적절한메소드를이용하여구하라.
5.스택(강의자료).key
 CHP 5: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ns-r91557ds ? (stack): (LIFO:Last-In First-Out):. D C B C B C B C B (element) C (top) B (bottom) (DT) : n element : create() ::=. is_empty(s) ::=. is_full(s) ::=.
CHP 5: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ns-r91557ds ? (stack): (LIFO:Last-In First-Out):. D C B C B C B C B (element) C (top) B (bottom) (DT) : n element : create() ::=. is_empty(s) ::=. is_full(s) ::=.
ABC 10장
 10 장구조체와리스트처리 0 자기참조구조체 자기참조구조체는자기자신의형을참조하는포인터멤버를가짐 이러한자료구조를동적자료구조라고함 배열이나단순변수는일반적으로블록을진입할때메모리할당을받지만, 동적자료구조는기억장소관리루틴을사용하여명시적으로메모리할당을요구함 10-1 자기참조구조체 10-2 자기참조구조체 예제 struct list { int struct list a; data;
10 장구조체와리스트처리 0 자기참조구조체 자기참조구조체는자기자신의형을참조하는포인터멤버를가짐 이러한자료구조를동적자료구조라고함 배열이나단순변수는일반적으로블록을진입할때메모리할당을받지만, 동적자료구조는기억장소관리루틴을사용하여명시적으로메모리할당을요구함 10-1 자기참조구조체 10-2 자기참조구조체 예제 struct list { int struct list a; data;
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 8: 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue): 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게된다. 가장일반적인큐 : 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있다. 자료구조스택큐우선순위큐 삭제되는요소가장최근에들어온데이터가장먼저들어온데이터가장우선순위가높은데이터 응용분야 : 시뮬레이션시스템 ( 여기서의우선순위는대개사건의시각이다.)
CHAP 8: 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue): 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게된다. 가장일반적인큐 : 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있다. 자료구조스택큐우선순위큐 삭제되는요소가장최근에들어온데이터가장먼저들어온데이터가장우선순위가높은데이터 응용분야 : 시뮬레이션시스템 ( 여기서의우선순위는대개사건의시각이다.)
4장
 CHAP 5: 스택 스택이란? 스택 (stack): 쌓아놓은더미 스택의특징 후입선출 (LIFO:Last-In First-Out): 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감. D C B C B C B C B A A A A 스택의구조 요소 (element) C 스택상단 (top) B A 스택하단 (bottom) 스택추상데이터타입 (ADT) 객체 : n개의 element형의요소들의선형리스트
CHAP 5: 스택 스택이란? 스택 (stack): 쌓아놓은더미 스택의특징 후입선출 (LIFO:Last-In First-Out): 가장최근에들어온데이터가가장먼저나감. D C B C B C B C B A A A A 스택의구조 요소 (element) C 스택상단 (top) B A 스택하단 (bottom) 스택추상데이터타입 (ADT) 객체 : n개의 element형의요소들의선형리스트
Microsoft PowerPoint - 제11장 포인터
 쉽게풀어쓴 C 언어 Express 제 11 장포인터 이번장에서학습할내용 포인터이란? 변수의주소 포인터의선언 간접참조연산자 포인터연산 포인터와배열 포인터와함수 이번장에서는포인터의기초적인지식을학습한다. 포인터란? 포인터 (pointer): 주소를가지고있는변수 1003 1004 1005 영화관 1002 1006 1001 포인터 (pointer) 1007 메모리의구조
쉽게풀어쓴 C 언어 Express 제 11 장포인터 이번장에서학습할내용 포인터이란? 변수의주소 포인터의선언 간접참조연산자 포인터연산 포인터와배열 포인터와함수 이번장에서는포인터의기초적인지식을학습한다. 포인터란? 포인터 (pointer): 주소를가지고있는변수 1003 1004 1005 영화관 1002 1006 1001 포인터 (pointer) 1007 메모리의구조
슬라이드 1
 CHAP 8: 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue): 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게된다. 우선순위큐 가장일반적인큐 : 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있다. 자료구조스택큐우선순위큐 삭제되는요소가장최근에들어온데이터가장먼저들어온데이터가장우선순위가높은데이터 응용분야 : 시뮬레이션시스템
CHAP 8: 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 우선순위큐 (priority queue): 우선순위를가진항목들을저장하는큐 FIFO 순서가아니라우선순위가높은데이터가먼저나가게된다. 우선순위큐 가장일반적인큐 : 스택이나 FIFO 큐를우선순위큐로구현할수있다. 자료구조스택큐우선순위큐 삭제되는요소가장최근에들어온데이터가장먼저들어온데이터가장우선순위가높은데이터 응용분야 : 시뮬레이션시스템
<4D F736F F F696E74202D20C1A63038C0E520C5ACB7A1BDBABFCD20B0B4C3BC4928B0ADC0C729205BC8A3C8AF20B8F0B5E55D>
 Power Java 제 8 장클래스와객체 I 이번장에서학습할내용 클래스와객체 객체의일생직접 메소드클래스를 필드작성해 UML 봅시다. QUIZ 1. 객체는 속성과 동작을가지고있다. 2. 자동차가객체라면클래스는 설계도이다. 먼저앞장에서학습한클래스와객체의개념을복습해봅시다. 클래스의구성 클래스 (class) 는객체의설계도라할수있다. 클래스는필드와메소드로이루어진다.
Power Java 제 8 장클래스와객체 I 이번장에서학습할내용 클래스와객체 객체의일생직접 메소드클래스를 필드작성해 UML 봅시다. QUIZ 1. 객체는 속성과 동작을가지고있다. 2. 자동차가객체라면클래스는 설계도이다. 먼저앞장에서학습한클래스와객체의개념을복습해봅시다. 클래스의구성 클래스 (class) 는객체의설계도라할수있다. 클래스는필드와메소드로이루어진다.
Microsoft PowerPoint - chap06-2pointer.ppt
 2010-1 학기프로그래밍입문 (1) chapter 06-2 참고자료 포인터 박종혁 Tel: 970-6702 Email: jhpark1@snut.ac.kr 한빛미디어 출처 : 뇌를자극하는 C프로그래밍, 한빛미디어 -1- 포인터의정의와사용 변수를선언하는것은메모리에기억공간을할당하는것이며할당된이후에는변수명으로그기억공간을사용한다. 할당된기억공간을사용하는방법에는변수명외에메모리의실제주소값을사용하는것이다.
2010-1 학기프로그래밍입문 (1) chapter 06-2 참고자료 포인터 박종혁 Tel: 970-6702 Email: jhpark1@snut.ac.kr 한빛미디어 출처 : 뇌를자극하는 C프로그래밍, 한빛미디어 -1- 포인터의정의와사용 변수를선언하는것은메모리에기억공간을할당하는것이며할당된이후에는변수명으로그기억공간을사용한다. 할당된기억공간을사용하는방법에는변수명외에메모리의실제주소값을사용하는것이다.
설계란 무엇인가?
 금오공과대학교 C++ 프로그래밍 jhhwang@kumoh.ac.kr 컴퓨터공학과 황준하 5 강. 배열, 포인터, 참조목차 배열 포인터 C++ 메모리구조 주소연산자 포인터 포인터연산 배열과포인터 메모리동적할당 문자열 참조 1 /20 5 강. 배열, 포인터, 참조배열 배열 같은타입의변수여러개를하나의변수명으로처리 int Ary[10]; 총 10 개의변수 : Ary[0]~Ary[9]
금오공과대학교 C++ 프로그래밍 jhhwang@kumoh.ac.kr 컴퓨터공학과 황준하 5 강. 배열, 포인터, 참조목차 배열 포인터 C++ 메모리구조 주소연산자 포인터 포인터연산 배열과포인터 메모리동적할당 문자열 참조 1 /20 5 강. 배열, 포인터, 참조배열 배열 같은타입의변수여러개를하나의변수명으로처리 int Ary[10]; 총 10 개의변수 : Ary[0]~Ary[9]
chap 5: Trees
 Chapter 5. TREES 목차 1. Introduction 2. 이진트리 (Binary Trees) 3. 이진트리의순회 (Binary Tree Traversals) 4. 이진트리의추가연산 5. 스레드이진트리 (Threaded Binary Trees) 6. 히프 (Heaps) 7. 이진탐색트리 (Binary Search Trees) 8. 선택트리 (Selection
Chapter 5. TREES 목차 1. Introduction 2. 이진트리 (Binary Trees) 3. 이진트리의순회 (Binary Tree Traversals) 4. 이진트리의추가연산 5. 스레드이진트리 (Threaded Binary Trees) 6. 히프 (Heaps) 7. 이진탐색트리 (Binary Search Trees) 8. 선택트리 (Selection
<443A5C4C C4B48555C B3E25C32C7D0B1E25CBCB3B0E8C7C1B7CEC1A7C6AE425CC0E7B0EDB0FCB8AE5C53746F636B5F4D616E D656E74732E637070>
 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 #include 6 #include "QuickSort.h" 7 using namespace std; 8 9 10 Node* Queue[100]; // 추가입력된데이터를저장하기위한 Queue
1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 #include 6 #include "QuickSort.h" 7 using namespace std; 8 9 10 Node* Queue[100]; // 추가입력된데이터를저장하기위한 Queue
Microsoft PowerPoint - 04-UDP Programming.ppt
 Chapter 4. UDP Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr http://ist.kunsan.ac.kr/ Dept. of Informatics & Statistics 목차 UDP 1 1 UDP 개념 자바 UDP 프로그램작성 클라이언트와서버모두 DatagramSocket 클래스로생성 상호간통신은 DatagramPacket 클래스를이용하여
Chapter 4. UDP Dongwon Jeong djeong@kunsan.ac.kr http://ist.kunsan.ac.kr/ Dept. of Informatics & Statistics 목차 UDP 1 1 UDP 개념 자바 UDP 프로그램작성 클라이언트와서버모두 DatagramSocket 클래스로생성 상호간통신은 DatagramPacket 클래스를이용하여
A Dynamic Grid Services Deployment Mechanism for On-Demand Resource Provisioning
 C Programming Practice (II) Contents 배열 문자와문자열 구조체 포인터와메모리관리 구조체 2/17 배열 (Array) (1/2) 배열 동일한자료형을가지고있으며같은이름으로참조되는변수들의집합 배열의크기는반드시상수이어야한다. type var_name[size]; 예 ) int myarray[5] 배열의원소는원소의번호를 0 부터시작하는색인을사용
C Programming Practice (II) Contents 배열 문자와문자열 구조체 포인터와메모리관리 구조체 2/17 배열 (Array) (1/2) 배열 동일한자료형을가지고있으며같은이름으로참조되는변수들의집합 배열의크기는반드시상수이어야한다. type var_name[size]; 예 ) int myarray[5] 배열의원소는원소의번호를 0 부터시작하는색인을사용
